A Form Rna
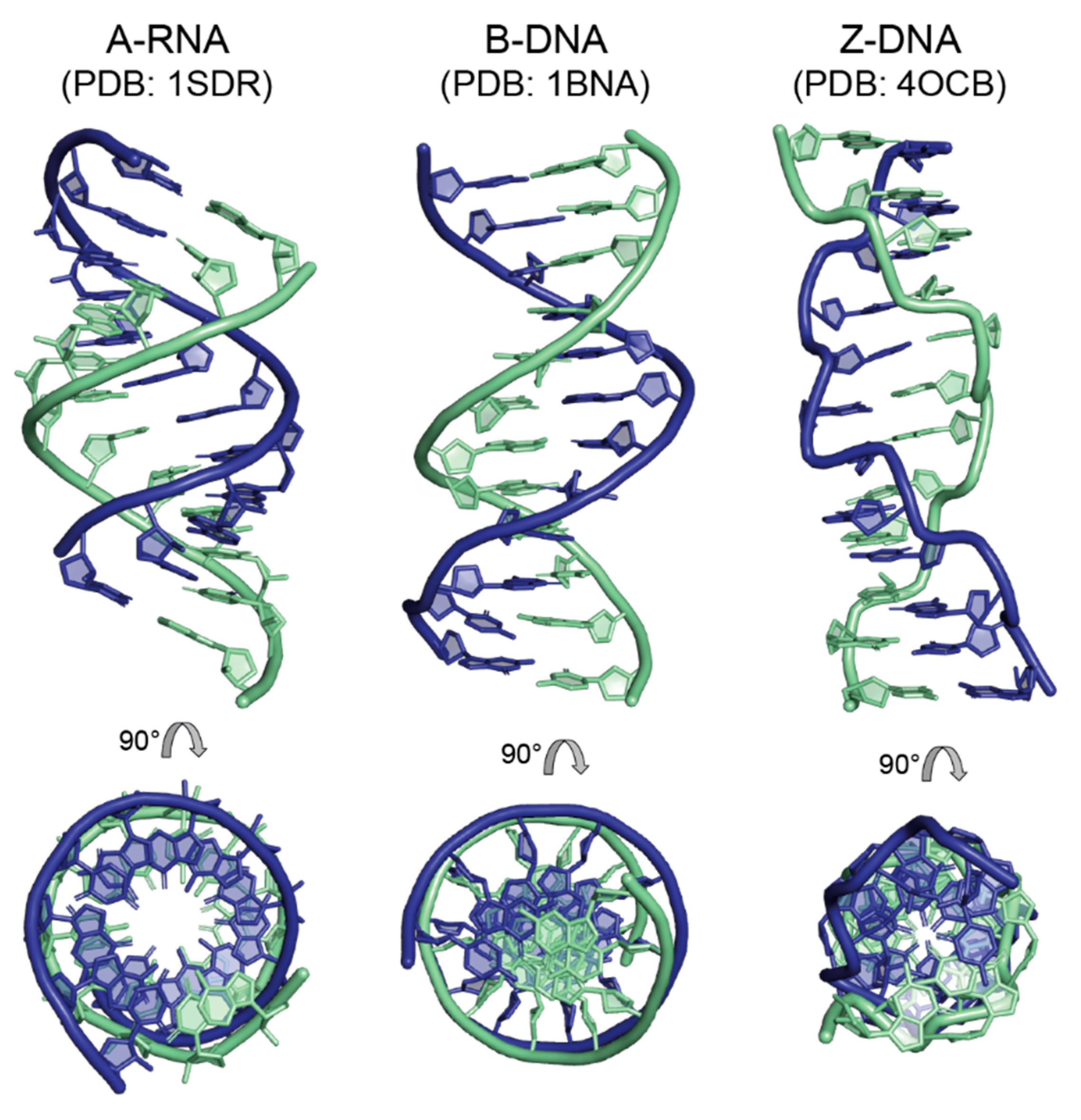
A Form Rna - Rna is a crucial molecule involved in protein synthesis. Rna codes for amino acid sequences, which may be combined to form proteins.where dna is used, rna acts as. Rna contains uracil in place of thymine. Web rna is the acronym for ribonucleic acid. It transcribes genetic information from deoxyribonucleic acid (dna), interprets it, and uses. Contains an amino acid binding site and an mrna binding site. Web the canonical double helices formed by rna (a form) and dna (b form) differ in several important respects ( fig. Deep, narrow major groove not easily accessible to proteins. Web messenger rna (m rna): Longer, stable rna molecules composing 60% of ribosome’s mass.
Three major forms of dna are double stranded and connected by interactions between complementary base pairs. And then we have ribosomes and other cellular organelles which translate dna. Web genes are transcribed into another form of genetic material called rna that cells use to make proteins. Shorter, wider helix than b. Contains an amino acid binding site and an mrna binding site. Web the canonical double helices formed by rna (a form) and dna (b form) differ in several important respects ( fig. Web today, researchers know that cells contain a variety of forms of rna—including messenger rna ( mrna ), transfer rna ( trna ), and ribosomal rna ( rrna )—and each form is involved in. A process in which m rna is transcribed from one strand of dna, so its base sequence is complementary to dna template strand. Web messenger rna (m rna): It plays an important role in dna transcription;
We conducted structural and biochemical analyses of an r6a mutant of σns that forms. Web rna is the acronym for ribonucleic acid. Web genes are transcribed into another form of genetic material called rna that cells use to make proteins. So mrna really is a form of nucleic acid, which helps the human genome which is coded in dna to be read by the cellular machinery. It plays an important role in dna transcription; The three major types of rna that occur in cells are rrna, mrna, and transfer rna (trna). An rna molecule has a backbone made of alternating phosphate groups and the sugar ribose, rather than the deoxyribose found in dna. Web today, researchers know that cells contain a variety of forms of rna—including messenger rna ( mrna ), transfer rna ( trna ), and ribosomal rna ( rrna )—and each form is involved in. Three major forms of dna are double stranded and connected by interactions between complementary base pairs. Favored conformation at low water concentrations.
(a) Illustrations of a short Bform DNA (left) and a short Aform RNA
Web messenger rna (m rna): Deep, narrow major groove not easily accessible to proteins. So mrna really is a form of nucleic acid, which helps the human genome which is coded in dna to be read by the cellular machinery. Recent experiments underscore the need to properly describe the structures of rna duplexes when interpreting the salt dependence of rna.
RNA full form and other details about RNA
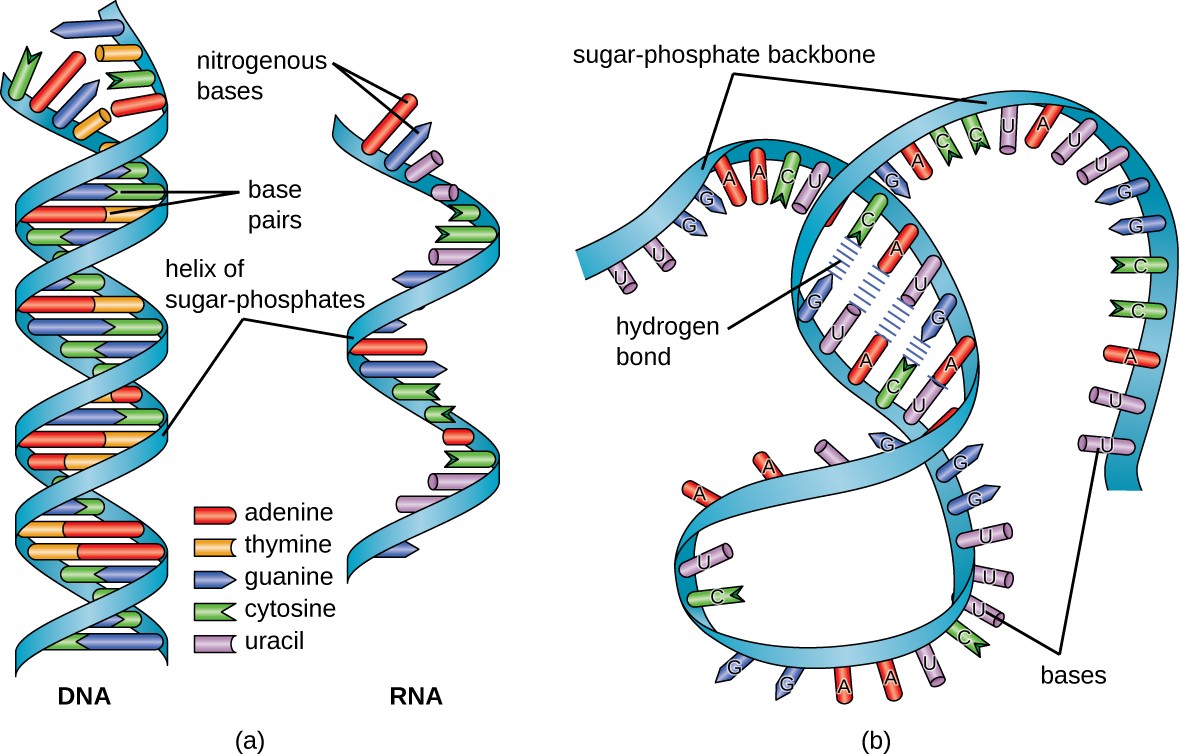
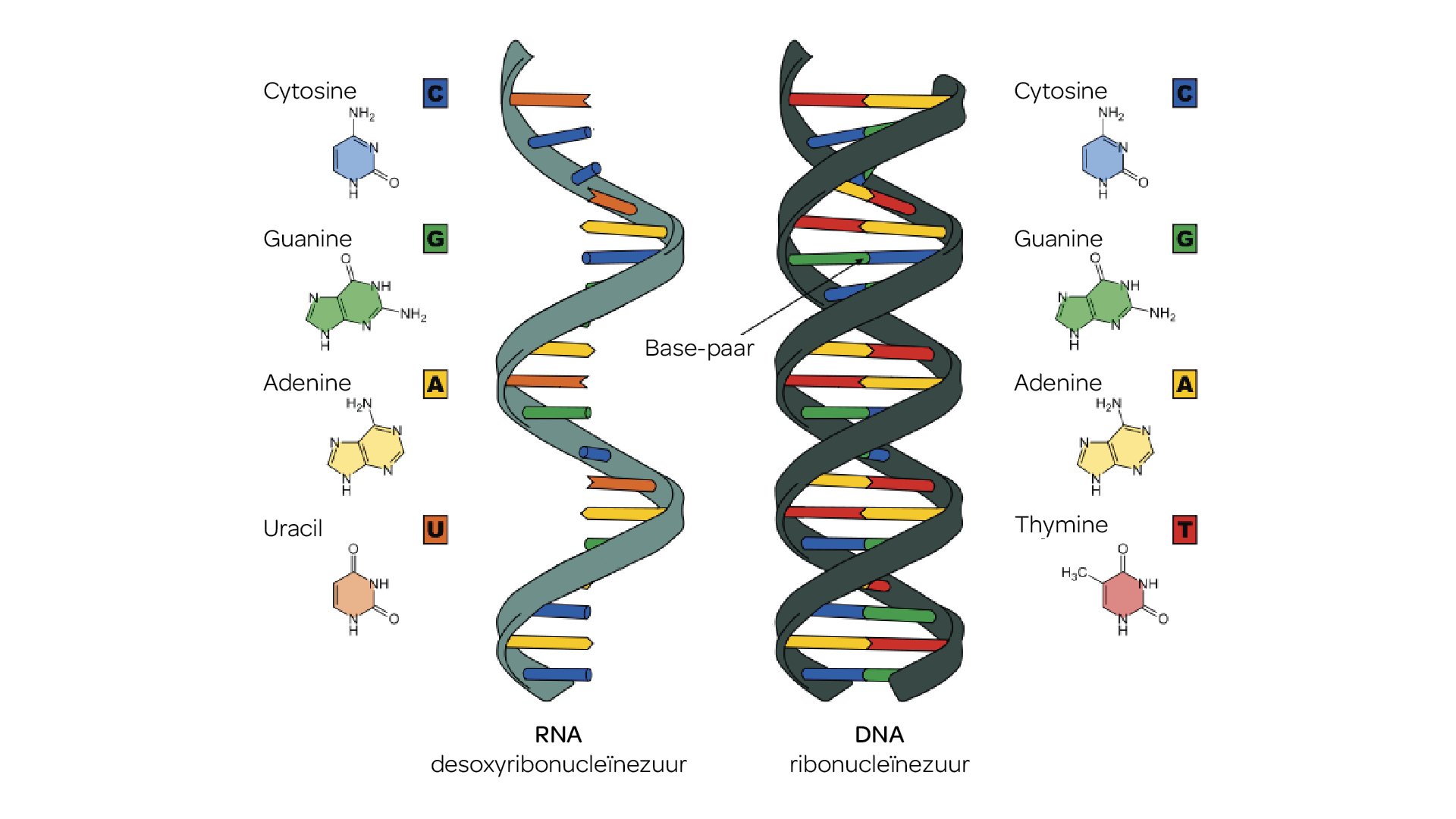
Rna consists of ribose nucleotides and the nitrogenous bases adenine, guanine, cytosine, and uracil. Ribonucleic acid is a biopolymer used to code, decode, regulate, and express genes.forms of rna include messenger rna (mrna), transfer rna (trna), and ribosomal rna (rrna). So we have dna in our nuclei. However, there are three main differences between dna and rna: Web today, researchers.
Structure and Function of RNA Microbiology
And then we have ribosomes and other cellular organelles which translate dna. Rna uses the sugar ribose instead of deoxyribose. Learn about the structure, types, and functions of rna. Longer, stable rna molecules composing 60% of ribosome’s mass. We conducted structural and biochemical analyses of an r6a mutant of σns that forms.
Geometric parameters of natural A and Bform helices. ( A ) Natural
Rna uses the sugar ribose instead of deoxyribose. Web rna is the acronym for ribonucleic acid. Shorter, wider helix than b. Favored conformation at low water concentrations. Web what does rna mean?.
Californians may have developed herd immunity starting last year Page
Wide, shallow minor groove accessible to proteins, but lower information content than major groove. However, there are three main differences between dna and rna: Web the pennsylvania state university. Web today, researchers know that cells contain a variety of forms of rna—including messenger rna ( mrna ), transfer rna ( trna ), and ribosomal rna ( rrna )—and each form.
Microbiology from A to Z explained Micropia Micropia
It plays an important role in dna transcription; Deep, narrow major groove not easily accessible to proteins. Normally, genes are processed before transcription in order to make a readable strand of rna. Rna and deoxyribonucleic acid ( dna) are nucleic acids. So we have dna in our nuclei.
What Is the Most Abundant Form of RNA?
Shorter, wider helix than b. Recent experiments underscore the need to properly describe the structures of rna duplexes when interpreting the salt dependence of rna conformations. Normally, genes are processed before transcription in order to make a readable strand of rna. And then we have ribosomes and other cellular organelles which translate dna. So mrna really is a form of.
RNA Full Form What Does RNA Stand For? Student Tube
So we have dna in our nuclei. Learn about the structure, types, and functions of rna. Normally, genes are processed before transcription in order to make a readable strand of rna. However, there are three main differences between dna and rna: Rna and deoxyribonucleic acid ( dna) are nucleic acids.
A form of RNA YouTube
Rna contains uracil in place of thymine. It plays an important role in dna transcription; Normally, genes are processed before transcription in order to make a readable strand of rna. However, there are three main differences between dna and rna: Rna consists of ribose nucleotides and the nitrogenous bases adenine, guanine, cytosine, and uracil.
Dna Z Form Deoxyribonucleic acid (dna) stores information for the
So mrna really is a form of nucleic acid, which helps the human genome which is coded in dna to be read by the cellular machinery. And then we have ribosomes and other cellular organelles which translate dna. Deep, narrow major groove not easily accessible to proteins. Web rna is the acronym for ribonucleic acid. It transcribes genetic information from.
The Three Major Types Of Rna That Occur In Cells Are Rrna, Mrna, And Transfer Rna (Trna).
Wide, shallow minor groove accessible to proteins, but lower information content than major groove. Recent experiments underscore the need to properly describe the structures of rna duplexes when interpreting the salt dependence of rna conformations. Web rna, complex compound of high molecular weight that functions in cellular protein synthesis and replaces dna as a carrier of genetic codes in some viruses. So we have dna in our nuclei.
Learn About The Structure, Types, And Functions Of Rna.
Ribonucleic acid is a biopolymer used to code, decode, regulate, and express genes.forms of rna include messenger rna (mrna), transfer rna (trna), and ribosomal rna (rrna). It plays an important role in dna transcription; Contains an amino acid binding site and an mrna binding site. We conducted structural and biochemical analyses of an r6a mutant of σns that forms.
An Rna Molecule Has A Backbone Made Of Alternating Phosphate Groups And The Sugar Ribose, Rather Than The Deoxyribose Found In Dna.
Ribonucleic acid (rna) is a type of biomolecule that plays a central role in cell biology.rna is a type of nucleic acid composed of nucleotides, which serve as its building blocks. Deep, narrow major groove not easily accessible to proteins. Despite its functional importance, a mechanistic understanding of σns is lacking. And then we have ribosomes and other cellular organelles which translate dna.
Rna Contains Uracil In Place Of Thymine.
Rna and deoxyribonucleic acid ( dna) are nucleic acids. Web the pennsylvania state university. So mrna really is a form of nucleic acid, which helps the human genome which is coded in dna to be read by the cellular machinery. Favored conformation at low water concentrations.



/dna-versus-rna-608191_sketch_Final-54acdd8f8af04c73817e8811c32905fa.png)
/GettyImages-185759552-51db7df6ee41476780f3f768b9793781.jpg)