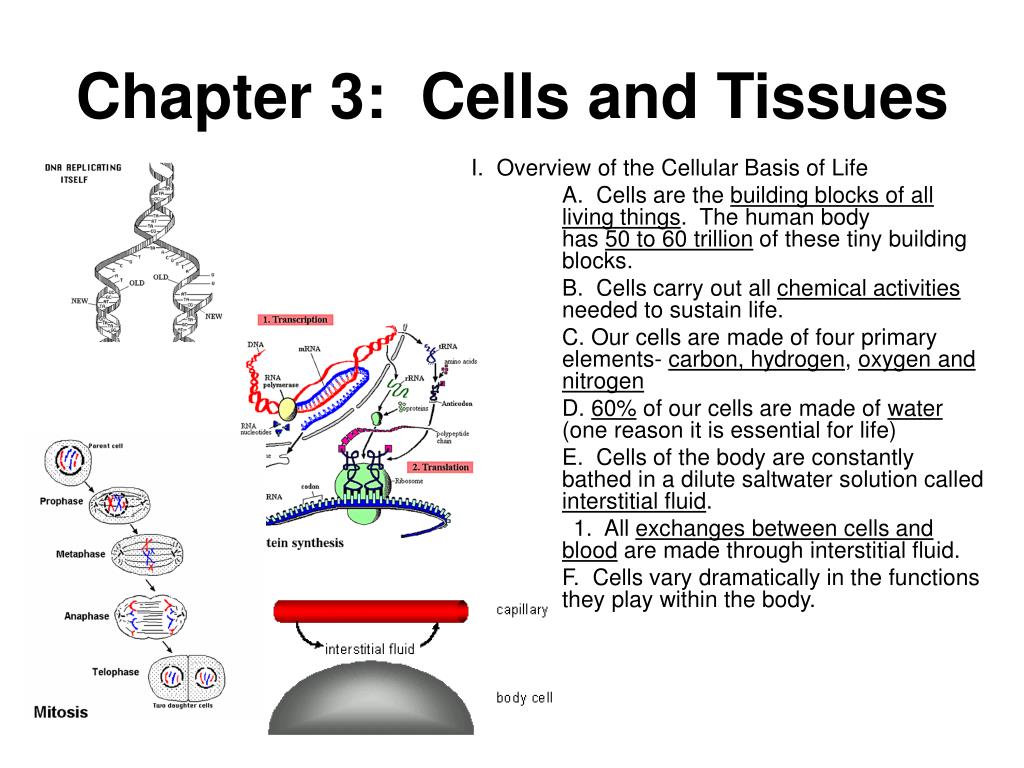
Chapter 3 Cells And Tissues
Chapter 3 Cells And Tissues - Micro tubules, actin filaments, intermediate filaments that give a cell shape and organize its parts. Control center of cell, contains dna, necessary for cell. Web terms in this set (50) cytoplasm. Web a concept that describes organelles and functions common to all cells. These different cell types form specialized tissues that work in concert to. Web the cells typical features: Cells and tissues chap 3. Muscles form the flesh of the body. Click the card to flip 👆. Web chapter 3 cells and tissues 49 4.
Click the card to flip 👆. Membrane made up of a double layer of lipids (phospholipids, cholesterol and so on) with proteins embedded within. The network of nuclear threads, composed of dna and protein, that condense to form chromosomes during mitosis is called. Name the 3 types of primary tissues & their function. Special cell membrane junctions are formed (tight junctions, desmosomes, gap junctions) tight junctions. Web terms in this set (50) cytoplasm. Substance of a cell other than the nucleus. Web the following lists terms and concepts that you should be familiar with from this chapter as it pertains to human anatomy and physiology. Web cells are the basic structural and functional units of all living organisms, activity of organism depends on activity of its cells, principle of complementarity, continuity of life has a cellular basis. Cook copyright 2003 pearson education, inc.
Publishing as benjamin cummings cells and tissues carry out all chemical activities needed tosustain life cells. Web the cells typical features: Briefly describe the form and function of three types of cytoskeletal filaments. Micro tubules, actin filaments, intermediate filaments that give a cell shape and organize its parts. Anatomy of the cell, cell extensions, cell diversity, cell physiology, life cycle of cell. Cook copyright 2003 pearson education, inc. Web cells are bound together in 3 ways. Web cells are the basic structural and functional units of all living organisms, activity of organism depends on activity of its cells, principle of complementarity, continuity of life has a cellular basis. Web identify the structures of a cell and their functions. Special cell membrane junctions are formed (tight junctions, desmosomes, gap junctions) tight junctions.
PPT Chapter 3 Cells and Tissues PowerPoint Presentation, free
Result in gross body movement. 3 main regions of the cell. Anatomy of the cell, cell extensions, cell diversity, cell physiology, life cycle of cell. The building blocks of all living things. Web • describe the structure/composition (matrix/cells) of each type of connective tissue discussed in the lecture notes.
Chapter 3 Cells and Tissues
Name the 3 types of primary tissues & their function. Cook copyright 2003 pearson education, inc. Briefly describe the form and function of three types of cytoskeletal filaments. Web chapter 3 cells and tissues test. Anatomy of the cell, cell extensions, cell diversity, cell physiology, life cycle of cell.
34 Chapter 3 Cells And Tissues Worksheet support worksheet
Web during this developmental process, early, undifferentiated cells differentiate and become specialized in their structure and function. Micro tubules, actin filaments, intermediate filaments that give a cell shape and organize its parts. Web cells are bound together in 3 ways. Web terms in this set (50) cytoplasm. Cook copyright 2003 pearson education, inc.
Chapter 3 Cells And Tissues Answer Key
Name the 3 types of primary tissues & their function. These different cell types form specialized tissues that work in concert to. Click the card to flip 👆. Cook copyright 2003 pearson education, inc. It is surrounded by the semifluid.
Anatomy Chapter 3 Cells And Tissues Worksheet Answer Key Anatomy
The tissue level of organization openstax textbook: Groups of cells that are similar in structure and function. Web cells are the basic structural and functional units of all living organisms, activity of organism depends on activity of its cells, principle of complementarity, continuity of life has a cellular basis. Glycoproteins in the glycocalyx act as an adhesive or cellular glue..
Cell Transport Study Guide Anatomy Answers
Web • describe the structure/composition (matrix/cells) of each type of connective tissue discussed in the lecture notes. All cells have 3 main regions, a nucleus, a plasma membrane, and the cytoplasm. Collections of cells and cell products that perform a relatively limited number of specialized functions. Web identify the structures of a cell and their functions. Membrane made up of.
Chapter 3 Cells And Tissues Answer Key
Web cells are the basic structural and functional units of all living organisms, activity of organism depends on activity of its cells, principle of complementarity, continuity of life has a cellular basis. Cook copyright 2003 pearson education, inc. It is surrounded by the semifluid. Web the cells typical features: Collections of cells and cell products that perform a relatively limited.
11+ Chapter 3 Cells And Tissues SireadMartine
Web identify the structures of a cell and their functions. Web • describe the structure/composition (matrix/cells) of each type of connective tissue discussed in the lecture notes. 3 regions include the nuclear membrane, nucleolus, and chromatin. Web cells are bound together in 3 ways. Web parts of chapter 3:
Chapter 3 Cells And Tissues Worksheet Answer Key
Web parts of chapter 3: Cells working together form tissues. Web a concept that describes organelles and functions common to all cells. Web the following lists terms and concepts that you should be familiar with from this chapter as it pertains to human anatomy and physiology. Glycoproteins in the glycocalyx act as an adhesive or cellular glue.
Chapter 3 Cells And Tissues Body Tissues Worksheet Answer Key
Briefly describe the form and function of three types of cytoskeletal filaments. It is surrounded by the semifluid. Web cells are the basic structural and functional units of all living organisms, activity of organism depends on activity of its cells, principle of complementarity, continuity of life has a cellular basis. The network of nuclear threads, composed of dna and protein,.
It Is Surrounded By The Semifluid.
Publishing as benjamin cummings cells and tissues carry out all chemical activities needed tosustain life cells. Groups of cells similar in structure that perform common or related function. The building blocks of all living things. Name the 3 types of primary tissues & their function.
Terms In This Set (64) Cells.
Control center of cell, contains dna, necessary for cell. 3 main regions of the cell. Specialized compartments within the cytosol of the cell. Web cells are the basic structural and functional units of all living organisms, activity of organism depends on activity of its cells, principle of complementarity, continuity of life has a cellular basis.
Special Cell Membrane Junctions Are Formed (Tight Junctions, Desmosomes, Gap Junctions) Tight Junctions.
Web identify the structures of a cell and their functions. The network of nuclear threads, composed of dna and protein, that condense to form chromosomes during mitosis is called. Result in gross body movement. Groups of cells that are similar in structure and function.
Web During This Developmental Process, Early, Undifferentiated Cells Differentiate And Become Specialized In Their Structure And Function.
Collections of cells and cell products that perform a relatively limited number of specialized functions. These different cell types form specialized tissues that work in concert to. Web chapter 3 cells and tissues test. All cells have 3 main regions, a nucleus, a plasma membrane, and the cytoplasm.