Chromosomes Uncoil To Form Chromatin
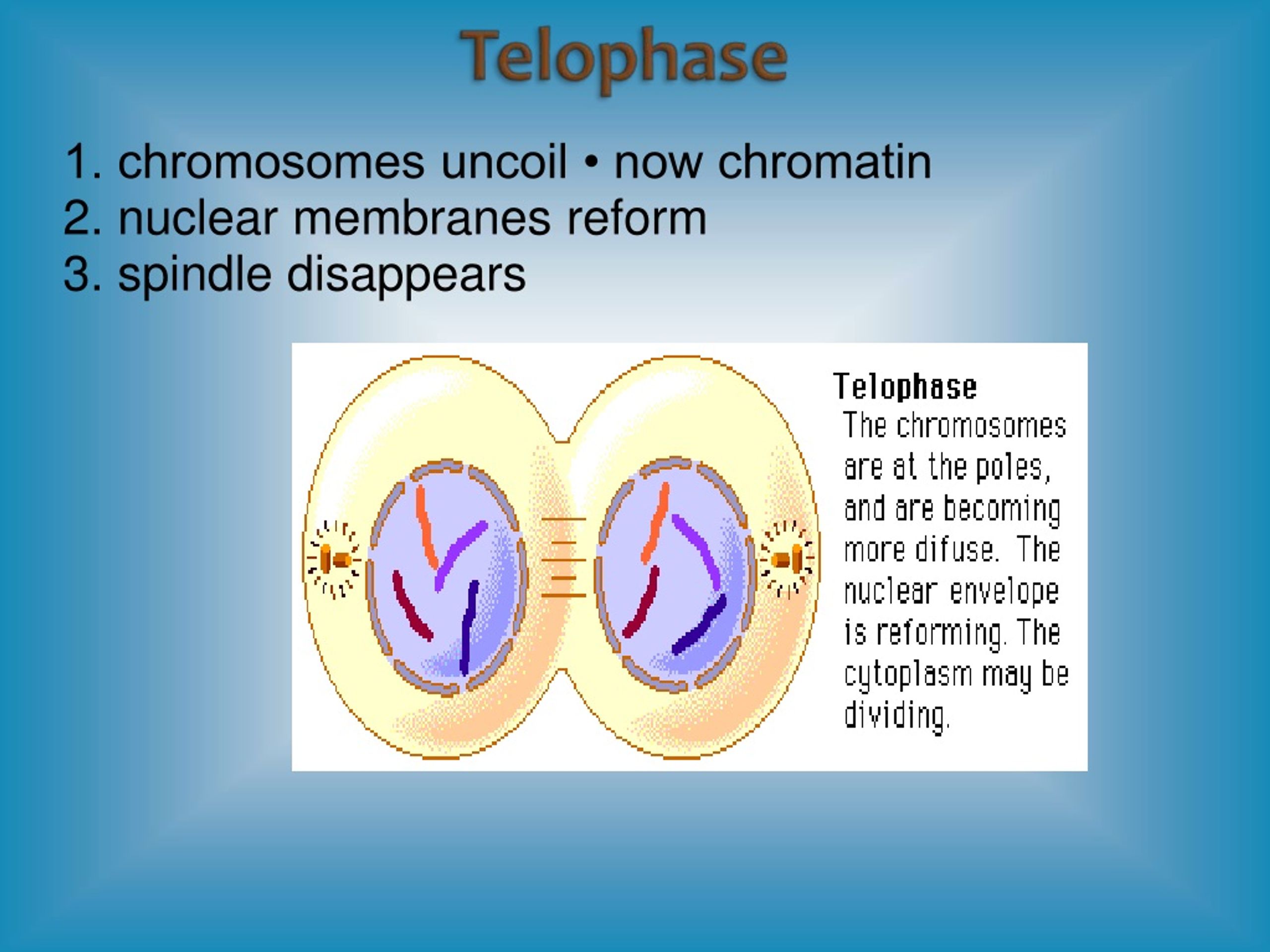
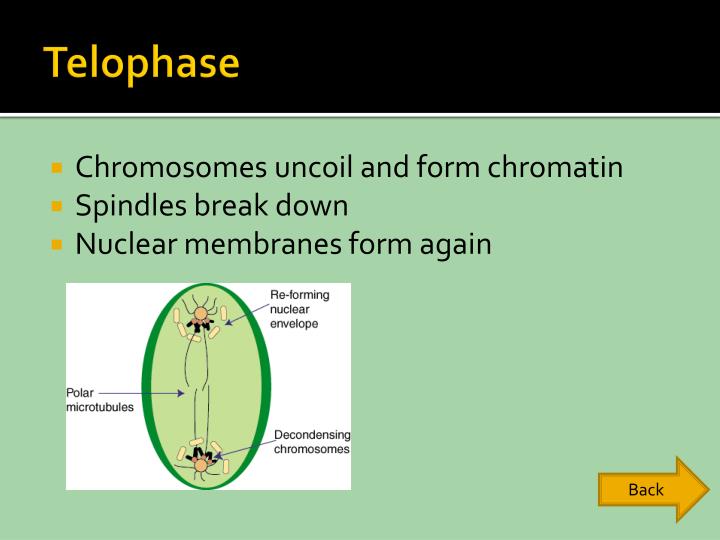
Chromosomes Uncoil To Form Chromatin - Dna, histones, and chromatin the answer to this question lies in the fact that certain proteins compact chromosomal dna into the microscopic space of the eukaryotic nucleus. Nuclear membrane and nucleolus disintegrate 4 chromosomes align on the spindle equator centrioles move to opposite ends of the cell. During the telophase phase, the chromosomes begin to uncoil. Chromatin fibers of chromosomes uncoil. The genetic contents of one cell have been divided. There are six phases with mitosis and telophase is number four. **cell looks like its being pinched. Web at the telophase of meiotic and mitotic cell divisions, the chromosomes of daughter cells uncoil back to chromatin, but after interphase, it coils up again to form visible chromosomes. Chromosomal centromeres split and chromosomes migrate to opposite ends metaphase of the cell. Nuclear membrane and nucleolus disintegrate.
Distinct chromosomes are often not visible and nuclear membranes may be present. Chromosomes uncoil to form chromatin. Web telophase chromosomes uncoil to form chromatin. How is all of this dna packaged so tightly into chromsomes and squeezed into a tiny nucleus? Web each of us has enough dna to reach from here to of daylight and back, get than 300 times. **cell looks like its being pinched. Chromatin fibers are coiled and condensed to form chromosomes. Web at the telophase of meiotic and mitotic cell divisions, the chromosomes of daughter cells uncoil back to chromatin, but after interphase, it coils up again to form visible chromosomes. During the telophase phase, the chromosomes begin to uncoil. Spindle fibers break downward, nuclear membrane application, and chromosomes getting to uncoil and application chromatin.
Chromatin fibers of chromosomes uncoil. How is all of this dna packaged so tightly into chromsomes and squeezed into a tiny nucleus? Web at the telophase of meiotic and mitotic cell divisions, the chromosomes of daughter cells uncoil back to chromatin, but after interphase, it coils up again to form visible chromosomes. Centrioles move to opposite ends of the cell. Web the nuclear envelopes of these nuclei form from remnant pieces of the parent cell's nuclear envelope and from pieces of the endomembrane system. There are six phases with mitosis and telophase is number four. Web each of us has enough dna to reach from here to of daylight and back, get than 300 times. Nuclear membrane and nucleolus disintegrate. After these changes, telophase/mitosis is largely complete. During the telophase phase, the chromosomes begin to uncoil.
Mechanisms in Psychiatric Disorders
Centrioles move to opposite ends of the cell. Chromosomal centromeres split and chromosomes migrate to opposite ends metaphase of the cell. Chromosomes uncoil to form chromatin a.) early prophase b.) telophase c.) anaphase d.) metaphase e.) late prophase Nuclear membrane and nucleolus disintegrate. Chromatin fibers are coiled and condensed to form chromosomes.
Chromosomes and chromatin YouTube
How is all of this dna packaged so tightly into chromsomes and squeezed into a tiny nucleus? The genetic contents of one cell have been divided. Dna, histones, and chromatin the answer to this question lies in the fact that certain proteins compact chromosomal dna into the microscopic space of the eukaryotic nucleus. Chromosomal centromeres split and chromosomes migrate to.
PPT Lesson Objectives—Cell Cycle PowerPoint Presentation, free
Nuclear membrane and nucleolus disintegrate 4 chromosomes align on the spindle equator centrioles move to opposite ends of the cell. Chromosomal centromeres split and chromosomes migrate to opposite ends metaphase of the cell. Web how is this possible? **cell looks like its being pinched. Isn't it simpler and more convenient for the chromosomes of the cells coil up in 1.
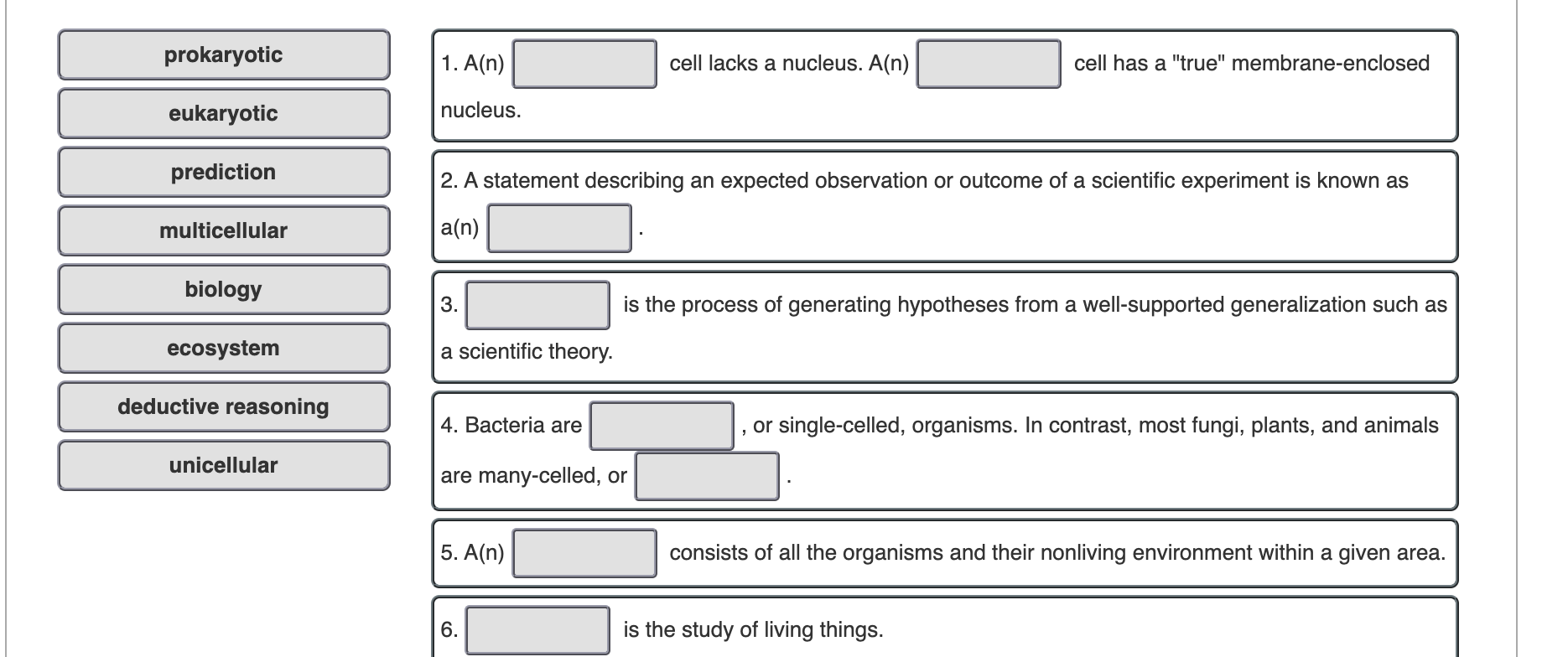
Solved Drag the terms on the left to the appropriate blanks
Chromosomes uncoil to form chromatin. Web at the telophase of meiotic and mitotic cell divisions, the chromosomes of daughter cells uncoil back to chromatin, but after interphase, it coils up again to form visible chromosomes. Web the nuclear envelopes of these nuclei form from remnant pieces of the parent cell's nuclear envelope and from pieces of the endomembrane system. Chromosomes.
PPT Stages of Mitosis PowerPoint Presentation ID4828392
**cell looks like its being pinched. Web each of us has enough dna to reach from here to of daylight and back, get than 300 times. Spindle fibers break downward, nuclear membrane application, and chromosomes getting to uncoil and application chromatin. Isn't it simpler and more convenient for the chromosomes of the cells coil up in 1 cell cycle? During.
modifications of chromatin structure. Chromosomes are
Centrioles move to opposite ends of the cell. The genetic contents of one cell have been divided. Web the nuclear envelopes of these nuclei form from remnant pieces of the parent cell's nuclear envelope and from pieces of the endomembrane system. Nuclear membrane and nucleolus disintegrate 4 chromosomes align on the spindle equator centrioles move to opposite ends of the.
Cell division, type of cell division, stages of nuclear division and
Web each of us has enough dna to reach from here to of daylight and back, get than 300 times. Chromosomal centromeres split and chromosomes migrate to opposite ends metaphase of the cell. During the telophase phase, the chromosomes begin to uncoil. **cell looks like its being pinched. Web a nucleosome consists of a dna sequence of about 150 base.
chromosomes chromatin Google Search med Pinterest
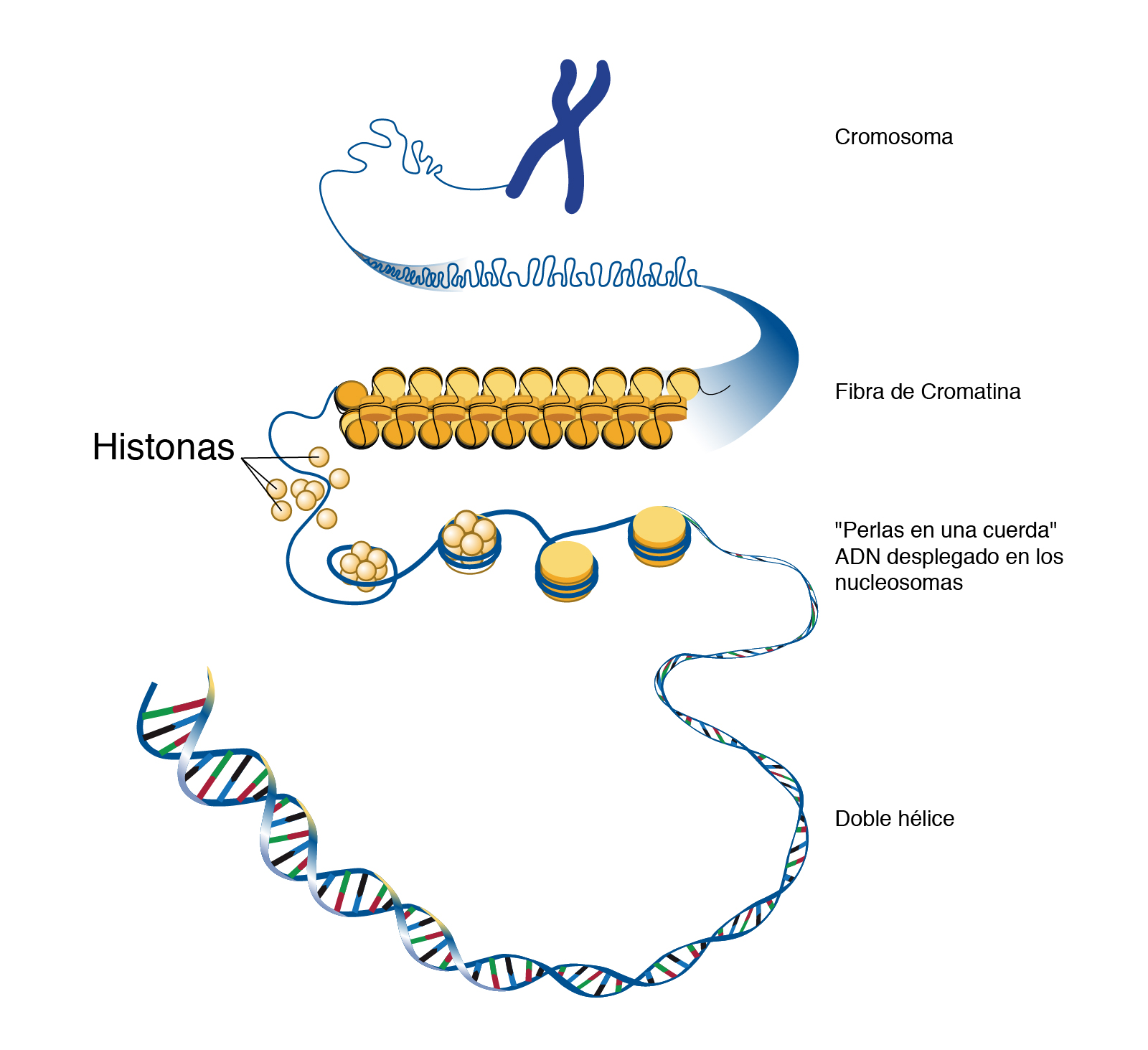
Web a nucleosome consists of a dna sequence of about 150 base pairs that is wrapped around a set of eight histones called an octamer. Web at the telophase of meiotic and mitotic cell divisions, the chromosomes of daughter cells uncoil back to chromatin, but after interphase, it coils up again to form visible chromosomes. Chromatin fibers of chromosomes uncoil..
Epigenomics approach illuminates the dark corners of the genome Broad
Web a nucleosome consists of a dna sequence of about 150 base pairs that is wrapped around a set of eight histones called an octamer. After these changes, telophase/mitosis is largely complete. Web at the telophase of meiotic and mitotic cell divisions, the chromosomes of daughter cells uncoil back to chromatin, but after interphase, it coils up again to form.
Biologia i geologia de 4rt U1 Compactació del DNA
During the telophase phase, the chromosomes begin to uncoil. Web each of us has enough dna to reach from here to of daylight and back, get than 300 times. Spindle fibers break downward, nuclear membrane application, and chromosomes getting to uncoil and application chromatin. Web the nuclear envelopes of these nuclei form from remnant pieces of the parent cell's nuclear.
Web Terms In This Set (90) 1.
Chromatin fibers are coiled and condensed to form chromosomes. Chromosomal centromeres split and chromosomes migrate to opposite ends metaphase of the cell. Spindle fibers break downward, nuclear membrane application, and chromosomes getting to uncoil and application chromatin. Nuclear membrane and nucleolus disintegrate.
Chromatin Fibers Of Chromosomes Uncoil.
During the telophase phase, the chromosomes begin to uncoil. The genetic contents of one cell have been divided. **cell looks like its being pinched. Web each of us has enough dna to reach from here to of daylight and back, get than 300 times.
Chromosomes Align On The Spindle Equator.
Web a nucleosome consists of a dna sequence of about 150 base pairs that is wrapped around a set of eight histones called an octamer. Nuclear membrane and nucleolus disintegrate 4 chromosomes align on the spindle equator centrioles move to opposite ends of the cell. Centrioles move to opposite ends of the cell. Distinct chromosomes are often not visible and nuclear membranes may be present.
Web How Is This Possible?
Isn't it simpler and more convenient for the chromosomes of the cells coil up in 1 cell cycle? After these changes, telophase/mitosis is largely complete. Dna, histones, and chromatin the answer to this question lies in the fact that certain proteins compact chromosomal dna into the microscopic space of the eukaryotic nucleus. Chromosomes uncoil to form chromatin a.) early prophase b.) telophase c.) anaphase d.) metaphase e.) late prophase