Halogens Tend To Form Anions Because
Halogens Tend To Form Anions Because - B) gaining electrons will fill. They have low first ionization energies b. B) gaining electrons will make them attain a. Web answered • expert verified. B) gaining electrons will fill their octet faster than losing them. Web c) halogen element ionization energies are lower than transition metal ionization energies. Web halogens tend to form anions because a) losing electrons will fill their octet faster than gaining them. They have low electron affinities c. Web + anions + chemistry. 1) they give up one electron to achieve the octet rule.
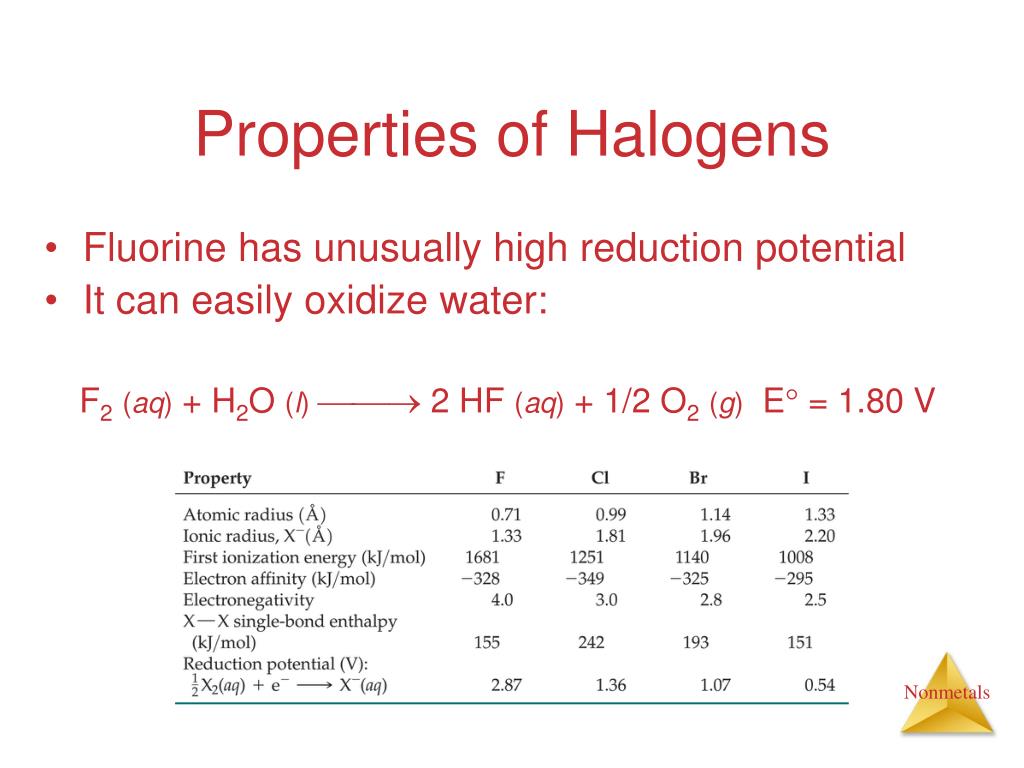
Most halogens are typically produced from minerals or salts. 0 followers · 0 following joined march 2020; Web c) halogen element ionization energies are lower than transition metal ionization energies. Halogens tend to form anions because a) losing electrons will fill their octet faster than gaining them. B) gaining electrons will make them attain a. Web all of the halogens form acids when bonded to hydrogen. Why does halogen tend to form an anion? Option b halogens have 7. Well, your question might actually require a direct answer but let me try expounding it in a better understandable way. Web halogenation is a term that refers to a chemical process that involves the addition of one or more halogens to a substance or a compound.
They have low electron affinities c. The halogens do exist in the +1 oxidation state, for example, in oclx− o c l x −. They have high electron affinities d. Web + anions + chemistry. The stoichiometry and route of. Web halogens tend to form anions because a) losing electrons will make them attain a noble gas configuration faster than gaining them. To begin with, halogens are those elements found in group 17 ( fomerly group 7) of the periodic table and they include; Halogens tend to form anions because a) losing electrons will fill their octet faster than gaining them. 1) they give up one electron to achieve the octet rule. Most halogens are typically produced from minerals or salts.
Cations And Anions List Tips to memorize cations YouTube
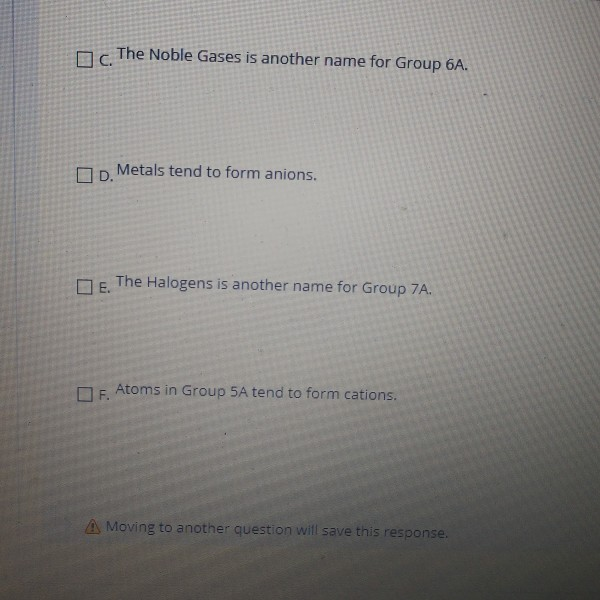
D) halogen atomic radii tend to be larger than their corresponding ionic radii. Web generally speaking the elements in the top right side of the periodic table (the nonmetals and halogens) tend to form anions. New york omvm omv η λίσοι estemos question 7 of 25 halogens tend to form anions because a) losing electrons. They have high electron affinities.
Constants I Periodic Table Learning Goal To familiar with the
New york omvm omv η λίσοι estemos question 7 of 25 halogens tend to form anions because a) losing electrons. B) gaining electrons will make them attain a. B) gaining electrons will fill their octet faster than losing them. C) anions are usually larger than their corresponding atom. Choose the false statement ( read carefully ) a.
anion Common anions, their names, formulas and the elements they are
The middle halogens—chlorine, bromine, and. Web + anions + chemistry. However, you aren't likely to see a naked xx+ x x +. D) halogen atomic radii tend to be larger than their corresponding ionic radii. B) gaining electrons will make them attain a.
Solved 13Atoms Of The Elements N And P Have Athe Same
Web halogens (flourine, chlorine, bromine, iodine, astatine) and oxygen tend to form anions when bonding with other elements. New york omvm omv η λίσοι estemos question 7 of 25 halogens tend to form anions because a) losing electrons. As expected, these elements have certain properties in common. Web halogenation is a term that refers to a chemical process that involves.
PPT Group 17 The Halogens PowerPoint Presentation, free download
Web halogens (flourine, chlorine, bromine, iodine, astatine) and oxygen tend to form anions when bonding with other elements. 2) have 7 valence electrons and need one more. Halogens have 7 electrons in their valence shell, so they tend to gain 1 electron to fill their octet. Web halogens tend to form anions because a) losing electrons will make them attain.
Solved Question 32 Which of the following statements about
B) gaining electrons will make them attain a. As expected, these elements have certain properties in common. B) gaining electrons will fill. C) anions are usually larger than their corresponding atom. Web halogens tend to form anions because a) losing electrons will fill their octet faster than gaining them.
PPT Chapter 22 Chemistry of the Nonmetals PowerPoint Presentation
D) halogen atomic radii tend to be larger than their corresponding ionic radii. Web halogens tend to form anions because a) losing electrons will fill their octet faster than gaining them. As expected, these elements have certain properties in common. The halogens do exist in the +1 oxidation state, for example, in oclx− o c l x −. 0 followers.
Which of the Following Exists as a Polyatomic Molecule
Web halogens tend to form anions because a) losing electrons will fill their octet faster than gaining them. Web halogens (flourine, chlorine, bromine, iodine, astatine) and oxygen tend to form anions when bonding with other elements. It is a subtle matter. B) gaining electrons will fill their octet faster than losing them. However, you aren't likely to see a naked.
Halogens tend to form anions because A) losing
As expected, these elements have certain properties in common. The stoichiometry and route of. Halogens have 7 electrons in their valence shell, so they tend to gain 1 electron to fill their octet. D) halogen atomic radii tend to be larger than their corresponding ionic radii. Web + anions + chemistry.
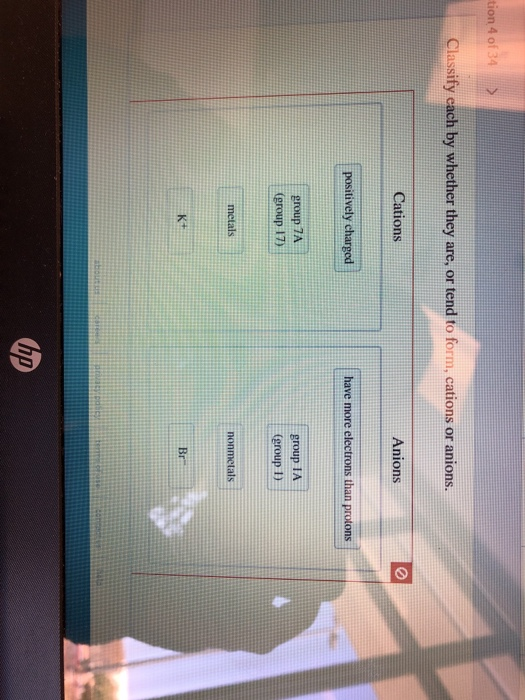
Solved tion 4 of 34 Classify each by whether they are, or
C) anions are usually larger than their corresponding atom. Web se cr ar ar the halogens tend to form anions because a. However, you aren't likely to see a naked xx+ x x +. 0 followers · 0 following joined march 2020; Web the halogens tend to form 1+ ions because they only need one electron to fill their valence.
Well, Your Question Might Actually Require A Direct Answer But Let Me Try Expounding It In A Better Understandable Way.
B) gaining electrons will fill their octet faster than losing them. Web se cr ar ar the halogens tend to form anions because a. Web halogens tend to form anions because a) losing electrons will fill their octet faster than gaining them. As expected, these elements have certain properties in common.
They Have Low First Ionization Energies B.
Web all of the halogens form acids when bonded to hydrogen. 2) have 7 valence electrons and need one more. New york omvm omv η λίσοι estemos question 7 of 25 halogens tend to form anions because a) losing electrons. Web answered • expert verified.
B) Gaining Electrons Will Make Them Attain A.
B) gaining electrons will fill. Web c) halogen element ionization energies are lower than transition metal ionization energies. Web the halogens tend to form 1+ ions because they only need one electron to fill their valence shell. Web generally speaking the elements in the top right side of the periodic table (the nonmetals and halogens) tend to form anions.
To Begin With, Halogens Are Those Elements Found In Group 17 ( Fomerly Group 7) Of The Periodic Table And They Include;
The stoichiometry and route of. Web + anions + chemistry. Halogens have 7 electrons in their valence shell, so they tend to gain 1 electron to fill their octet. Web halogenation is a term that refers to a chemical process that involves the addition of one or more halogens to a substance or a compound.