How Do Wetlands Form
How Do Wetlands Form - Web how do wetlands form? They help ease the effects of drought and wildfires by damming up streams and forming ponds. Web what are created wetlands? Web wetlands may also form in sink holes and other areas where percolating water has dissolved bedrock. Runoff travels down the side of a divide. Trees, root mats and other. How has the removal of wetlands impacted rivers and streams? Web wetlands are areas where water covers the soil, or is present either at or near the surface of the soil all year or for varying periods of time during the year,. What happens when a wetland dries. Web wetland hydrology (ground or surface water that inundates or saturates soils sufficiently to support a prevalence of hydrophytic vegetation).
Earthquakes can create wetlands by damming rivers or. Web wetlands form when water and land meet. Web wetlands are formed when the groundwater or overflow from nearby bodies of water flood the land. Saltwater march and mangrove forest. Web wetlands form the tributaries flow into rivers. They help ease the effects of drought and wildfires by damming up streams and forming ponds. Water builds up in a depression left by an ice sheet. Flooding of coastal lowlands from rising sea levels has created broad coastal marshes that are protected from wave action by barrier islands or reefs. How has the removal of wetlands impacted rivers and streams? Good news often called “nurseries of life,” wetlands provide habitat for.
Before a lot of the water has a chance to evaporate, more flooding occurs,. Wetlands form where water and land meet. Well, the last one, when groundwater comes up to the surface. Web 1 day agosome experts now see beavers — nature's helpers — as their dams can mitigate the effects of drought and wildfires. Web wetlands form the tributaries flow into rivers. Web how do wetlands form? Web wetlands form when water and land meet. Web wetlands are formed when the groundwater or overflow from nearby bodies of water flood the land. Web many pollutants are washed by rainfall from urban and agricultural lands and are carried overland to water bodies. Beavers are doing their part to mitigate.
Do Oil Companies Care About Protecting Alberta Wetlands? AiM Land
Two types of coastal wetlands. Web wetlands may also form in sink holes and other areas where percolating water has dissolved bedrock. Where do we see that it talks about water and land? Web what are created wetlands? Web a wetland is an area of land that is saturated with water either permanently or seasonally.
Natural Infrastructure — Ducks Unlimited Canada
Web a wetland is an area of land that is saturated with water either permanently or seasonally. Wetlands is a flat area of abundant herbaceous and/or shrubby vegetation that remains. Web here are some of the processes that form or modify wetlands: Groundwater comes to the surface and floods the land. Web 1 day agobeavers are doing their part to.
Why wetlands matter Wetlands International
Wetlands is a flat area of abundant herbaceous and/or shrubby vegetation that remains. How are wetlands beneficial to humans? Web wetlands are formed when the groundwater comes to the surface and floods the land. Saltwater march and mangrove forest. Web wetlands may also form in sink holes and other areas where percolating water has dissolved bedrock.
how wetlands work Wetland, Ecosystems, What is green
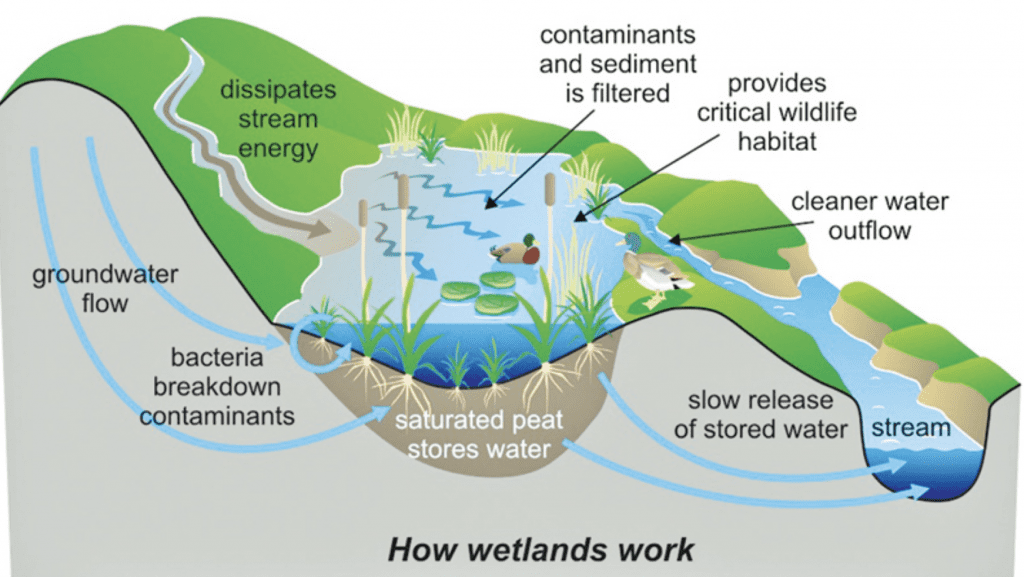
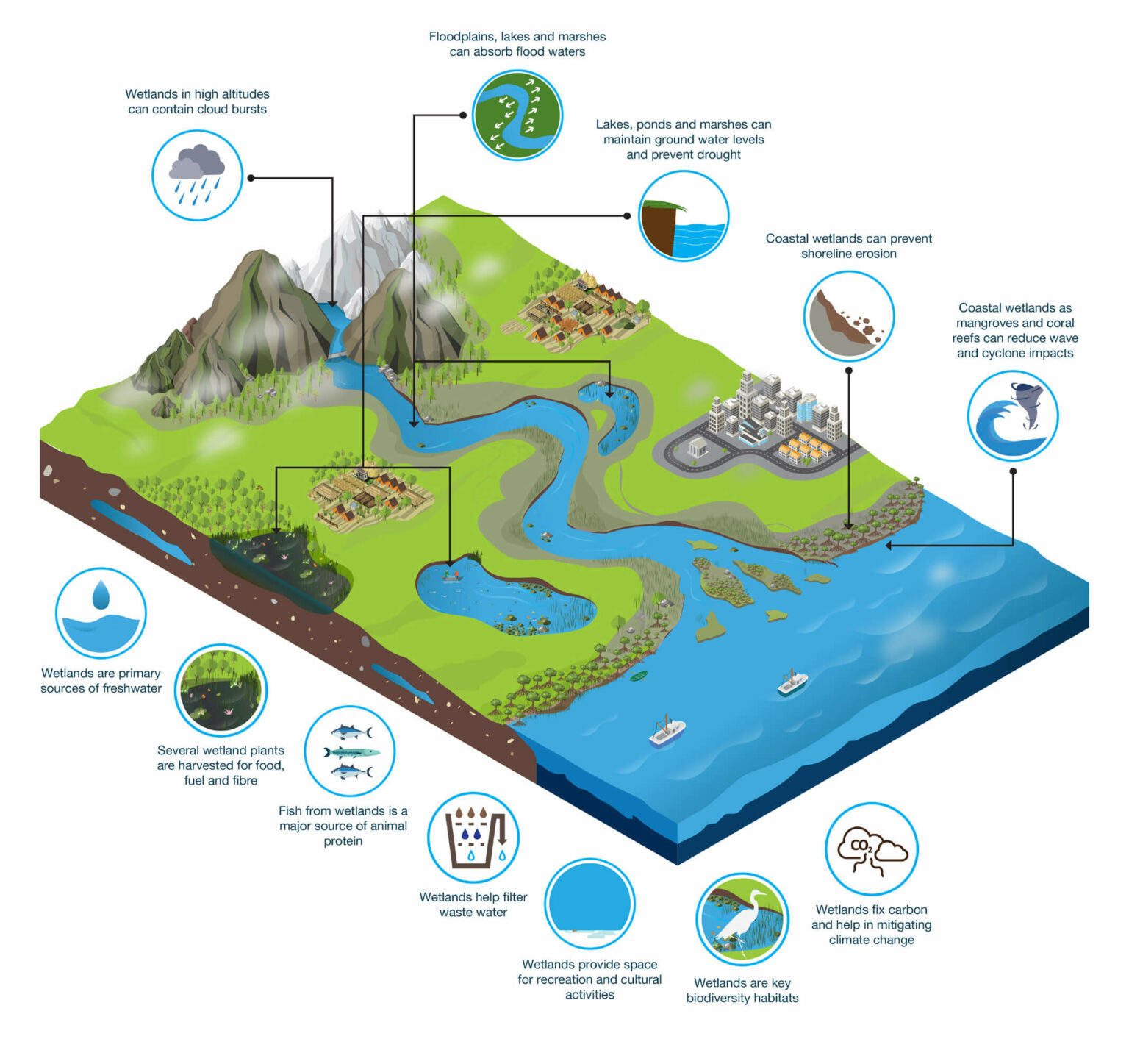
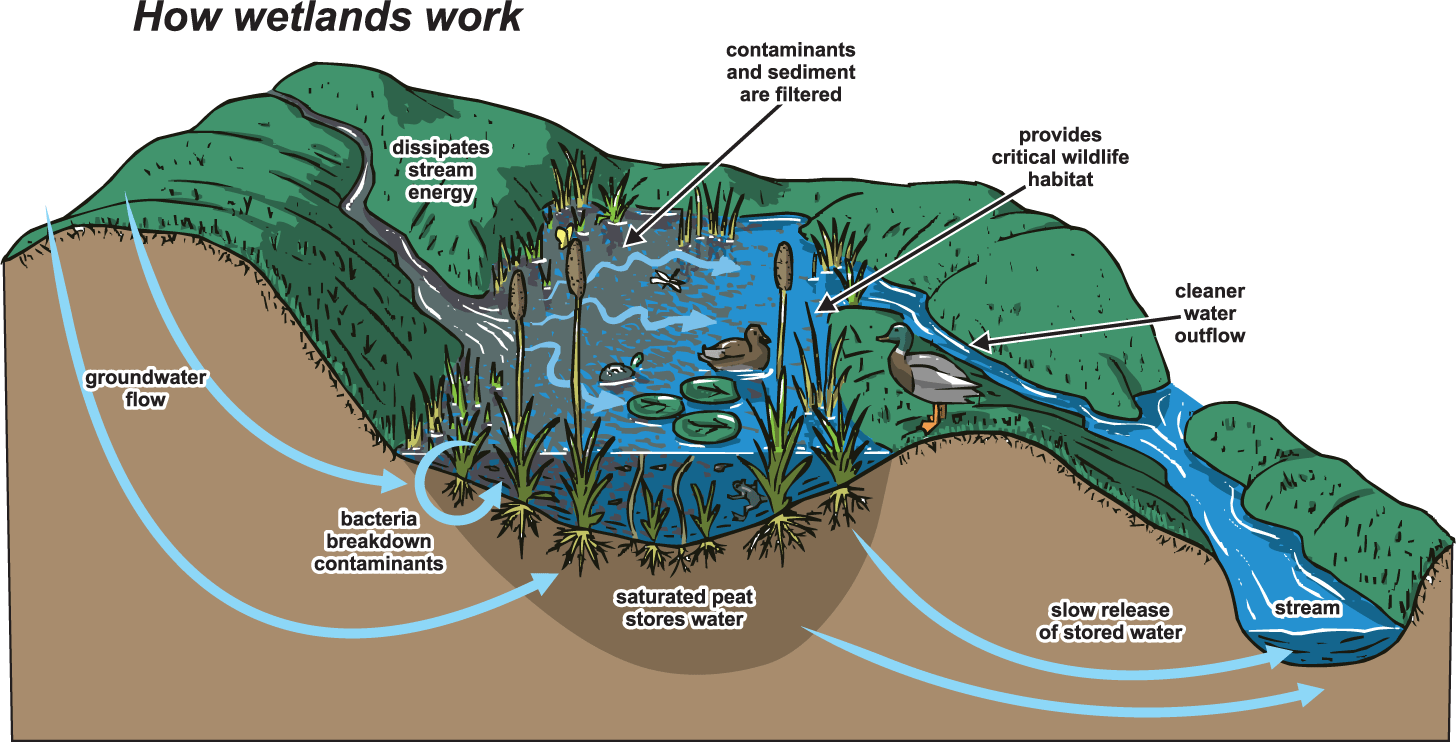
Web wetlands function as natural sponges that trap and slowly release surface water, rain, snowmelt, groundwater and flood waters. Well, the last one, when groundwater comes up to the surface. Wetlands form where water and land meet. Saltwater march and mangrove forest. Describe two ways that wetlands are important to living.
EPA Releases Report Showing Nearly Half of Nation’s Wetlands in Good
Web wetlands are formed when the groundwater or overflow from nearby bodies of water flood the land. Good news often called “nurseries of life,” wetlands provide habitat for. Earthquakes can create wetlands by damming rivers or. Where do we see that it talks about water and land? Web how do wetlands form?
Where Wetlands Form Kenilworth Park & Aquatic Gardens (U.S. National
Which freshwater source is a permanent shallow body of water with plant life throughout? Water builds up in a depression left by an ice sheet. Web wetlands are formed when the groundwater or overflow from nearby bodies of water flood the land. Wetlands is a flat area of abundant herbaceous and/or shrubby vegetation that remains. Web how do wetlands form?
The Role of Wetlands in Mitigating Flooding Biol4095 Applied Plant
Web wetlands are formed when the groundwater or overflow from nearby bodies of water flood the land. What happens when a wetland dries. Two types of coastal wetlands. Runoff travels down the side of a divide. Good news often called “nurseries of life,” wetlands provide habitat for.
Why Do We Need Wetlands? Does God Exist? Today
Two types of coastal wetlands. Web 1 day agobeavers are doing their part to mitigate climate change. Web wetlands are formed when the groundwater or overflow from nearby bodies of water flood the land. Web here are some of the processes that form or modify wetlands: Web many pollutants are washed by rainfall from urban and agricultural lands and are.
Making way for coastal wetlands a look at sea level rise and urban
Where do we see that it talks about water and land? Web wetland hydrology (ground or surface water that inundates or saturates soils sufficiently to support a prevalence of hydrophytic vegetation). What happens when a wetland dries. Wetlands is a flat area of abundant herbaceous and/or shrubby vegetation that remains. Which freshwater source is a permanent shallow body of water.
What are wetlands and how do they affect us? WastePlan
Runoff travels down the side of a divide. The areas adjacent to large water bodies like seas and rivers are. Web how do wetlands form? Web 1 day agosome experts now see beavers — nature's helpers — as their dams can mitigate the effects of drought and wildfires. Before a lot of the water has a chance to evaporate, more.
Web Wetlands Form The Tributaries Flow Into Rivers.
Wetlands is a flat area of abundant herbaceous and/or shrubby vegetation that remains. Web wetlands function as natural sponges that trap and slowly release surface water, rain, snowmelt, groundwater and flood waters. Web wetlands are formed when the groundwater comes to the surface and floods the land. Web a wetland is an area of land that is saturated with water either permanently or seasonally.
Web Here Are Some Of The Processes That Form Or Modify Wetlands:
Groundwater comes to the surface and floods the land. How are wetlands beneficial to humans? Wetlands can be freshwater, brackish (partly salty), or saline (very salty). Web wetland hydrology (ground or surface water that inundates or saturates soils sufficiently to support a prevalence of hydrophytic vegetation).
Well, The Last One, When Groundwater Comes Up To The Surface.
Web how do wetlands form? Good news often called “nurseries of life,” wetlands provide habitat for. Web wetlands form when water and land meet. The areas adjacent to large water bodies like seas and rivers are.
Web Many Pollutants Are Washed By Rainfall From Urban And Agricultural Lands And Are Carried Overland To Water Bodies.
Describe two ways that wetlands are important to living. What happens when a wetland dries. Flooding of coastal lowlands from rising sea levels has created broad coastal marshes that are protected from wave action by barrier islands or reefs. Wetlands form where water and land meet.