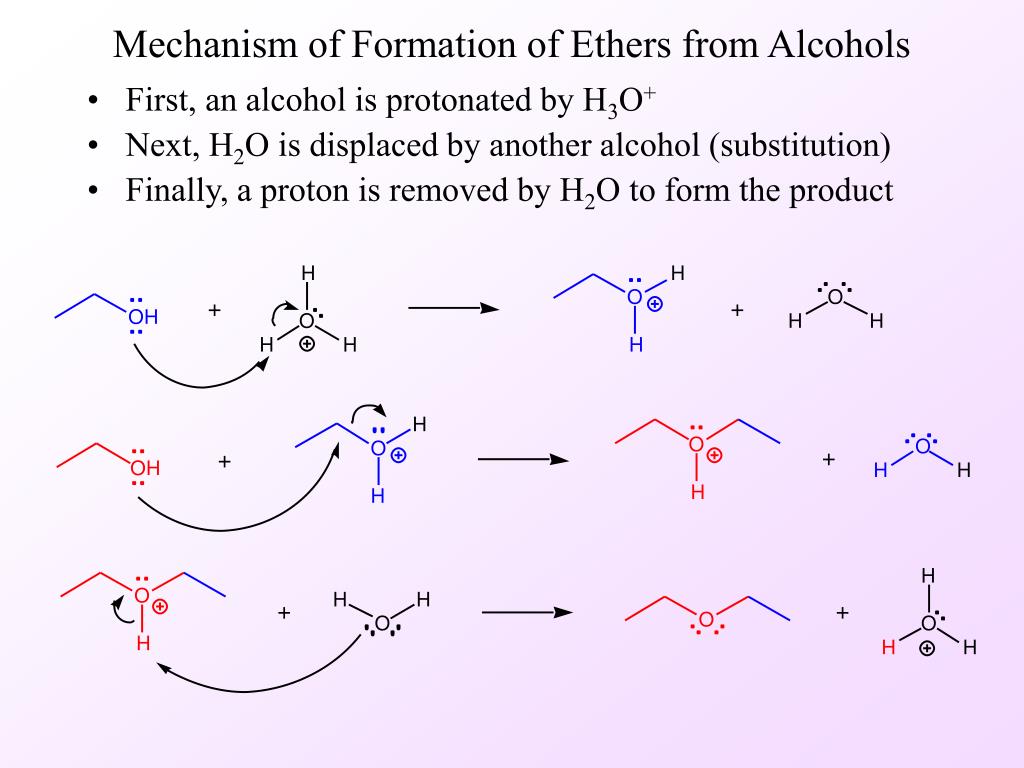
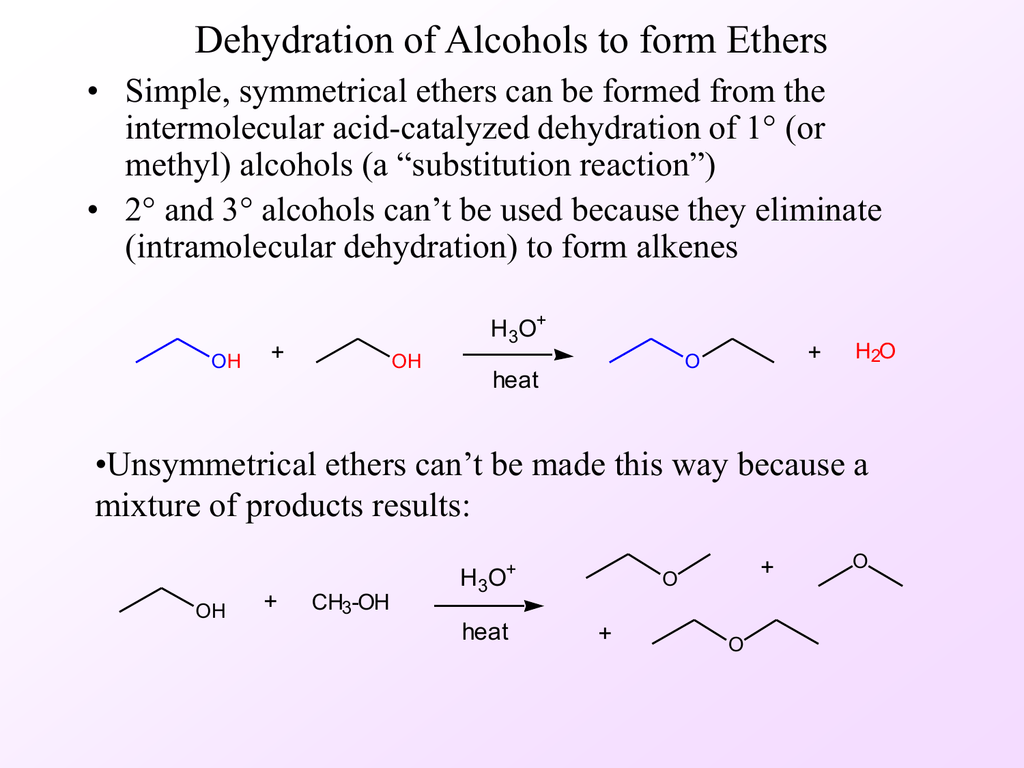
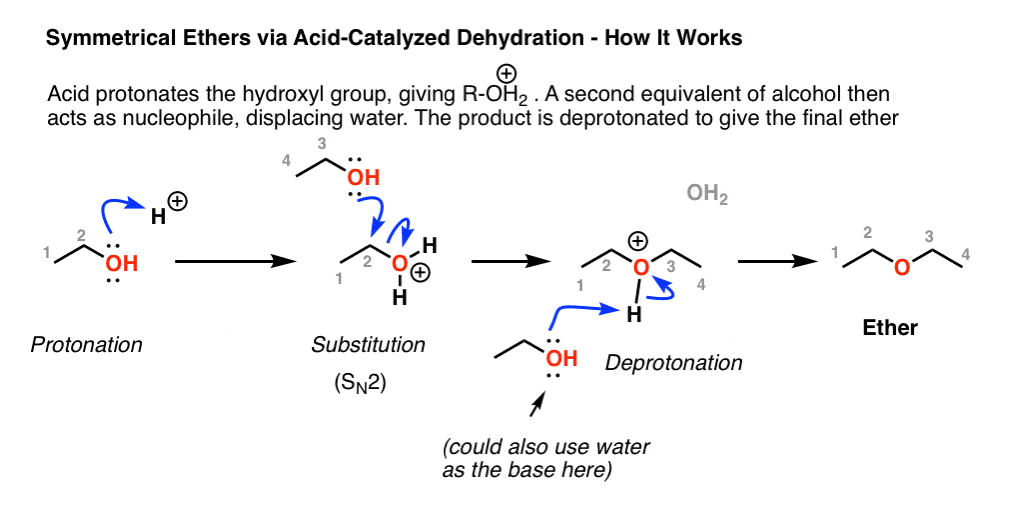
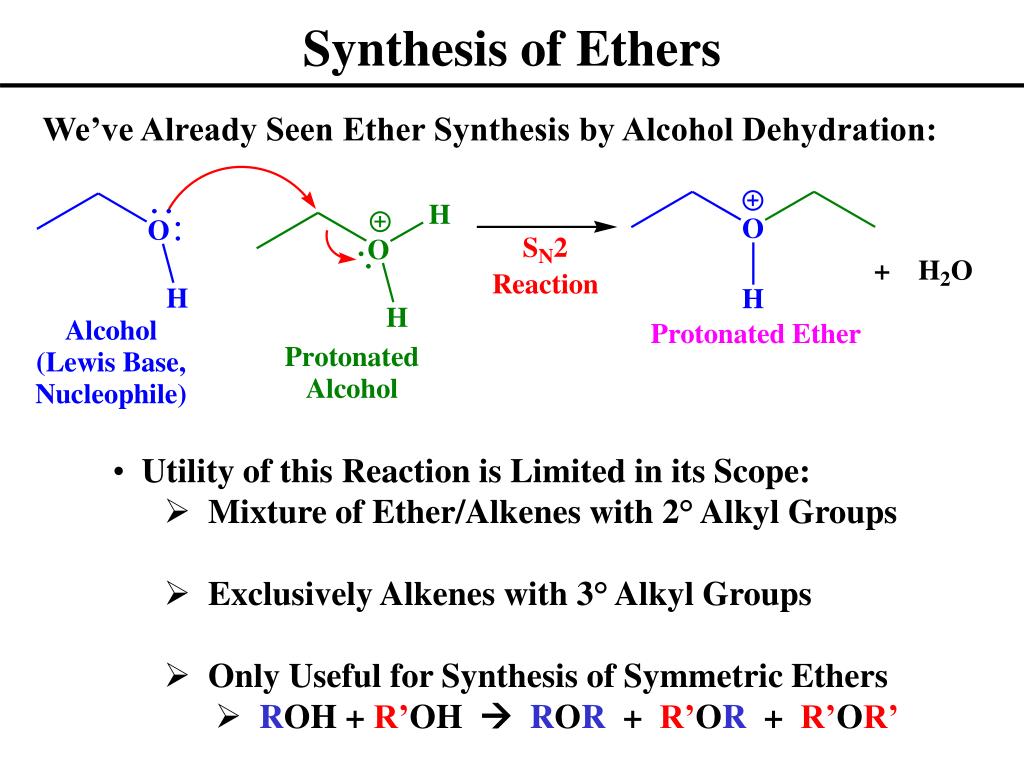
How To Form Ether From Alcohol
How To Form Ether From Alcohol - [noun] a compound that is both an ether and an alcohol. Then resulting halide conjugate base attacks the protonated ether at the less sterically hindered alkyl substituent forming a. Okay, but it's going to form on lee symmetrical ethers, okay? Web we will see that alcohols and ethers must be “activated” before they can undergo a substitution or elimination reaction. Identify the limitations of the williamson synthesis, and make the appropriate. Web it should say ethers. Web oxymercuration williamson ether synthesis study notes we studied oxymercuration as a method of converting an alkene to an alcohol in section 8.5. Web esters are produced when carboxylic acids are heated with alcohols in the presence of an acid catalyst. Some of them are discussed below, preparation of ethers by alcohol dehydration in this method, in the. Web the first name is the common name, in which you put the names of the alkyl groups before the word ether.
Okay, but it's going to form on lee symmetrical ethers, okay? Web oxymercuration williamson ether synthesis study notes we studied oxymercuration as a method of converting an alkene to an alcohol in section 8.5. When a mixture of t. Web ethers can be obtained from alcohols by the elimination of a molecule of water from two molecules of the alcohol. The alcohol's oxygen atom is protonated via an acid‐base reaction, leading to the formation of an oxonium ion. Sulfuric acid dissociates, giving a proton plus the bisulfate ion. And the reason is because we're always gonna be reacting acid in alcohol and you're gonna. Identify the limitations of the williamson synthesis, and make the appropriate. Describe the structure and properties of alcohols describe the structure and properties of ethers. Web learning objectives by the end of this section, you will be able to:
Web ethers can be obtained from alcohols by the elimination of a molecule of water from two molecules of the alcohol. (organic compound, uncountable) diethyl ether (c 4 h 10 o), a. The alcohol's oxygen atom is protonated via an acid‐base reaction, leading to the formation of an oxonium ion. Web we will see that alcohols and ethers must be “activated” before they can undergo a substitution or elimination reaction. Identify the limitations of the williamson synthesis, and make the appropriate. Ethyl alcohol reacts with alumina at 260 0c and gives diethyl ether. Web cbse study material textbook solutions live join vedantu’s free mastercalss preparation of ether with reactions and equations ether is a pleasant. Sulfuric acid dissociates, giving a proton plus the bisulfate ion. The catalyst is usually concentrated sulphuric acid. Web ethers can be prepared from organic compounds by various methods.
Alcohol & Ether, Lecture1, Problems discussion YouTube
Then resulting halide conjugate base attacks the protonated ether at the less sterically hindered alkyl substituent forming a. [noun] a compound that is both an ether and an alcohol. Web esters are produced when carboxylic acids are heated with alcohols in the presence of an acid catalyst. Web it should say ethers. The catalyst is usually concentrated sulphuric acid.
PPT Chapter 11 Alcohols and Ethers PowerPoint Presentation ID300959
Some of them are discussed below, preparation of ethers by alcohol dehydration in this method, in the. The catalyst is usually concentrated sulphuric acid. Identify the limitations of the williamson synthesis, and make the appropriate. (organic compound, uncountable) diethyl ether (c 4 h 10 o), a. Sulfuric acid dissociates, giving a proton plus the bisulfate ion.
Ethers NEB Grade 12 Notes Organic Chemistry Sajha Notes
Sulfuric acid dissociates, giving a proton plus the bisulfate ion. Ethyl alcohol reacts with alumina at 260 0c and gives diethyl ether. Web esters are produced when carboxylic acids are heated with alcohols in the presence of an acid catalyst. Web the first name is the common name, in which you put the names of the alkyl groups before the.
PPT Dehydration of Alcohols to form Ethers PowerPoint Presentation
And the reason is because we're always gonna be reacting acid in alcohol and you're gonna. Web esters are produced when carboxylic acids are heated with alcohols in the presence of an acid catalyst. Web we will see that alcohols and ethers must be “activated” before they can undergo a substitution or elimination reaction. Some of them are discussed below,.
Write the mechanism of acid dehydration of ethanol to yield ethene
Web ethers can be obtained from alcohols by the elimination of a molecule of water from two molecules of the alcohol. [noun] a compound that is both an ether and an alcohol. Okay, but it's going to form on lee symmetrical ethers, okay? (organic compound, uncountable) diethyl ether (c 4 h 10 o), a. Describe the structure and properties of.
Dehydration of Alcohols to form Ethers
Web first, the strong acid protonates the ether oxygen. (organic compound, countable) a compound containing an oxygen atom bonded to two hydrocarbon groups. Web ethers can be obtained from alcohols by the elimination of a molecule of water from two molecules of the alcohol. Then resulting halide conjugate base attacks the protonated ether at the less sterically hindered alkyl substituent.
Ethers by Dehydration of Alcohols YouTube
Web first, the strong acid protonates the ether oxygen. The alcohol's oxygen atom is protonated via an acid‐base reaction, leading to the formation of an oxonium ion. Then resulting halide conjugate base attacks the protonated ether at the less sterically hindered alkyl substituent forming a. Ethyl alcohol reacts with alumina at 260 0c and gives diethyl ether. Some of them.
Alcohols To Ethers via Acid Catalysis Master Organic Chemistry
Some of them are discussed below, preparation of ethers by alcohol dehydration in this method, in the. The alcohol's oxygen atom is protonated via an acid‐base reaction, leading to the formation of an oxonium ion. And the reason is because we're always gonna be reacting acid in alcohol and you're gonna. The catalyst is usually concentrated sulphuric acid. Web first,.
PPT Chapter 11 Alcohols and Ethers PowerPoint Presentation, free
[noun] a compound that is both an ether and an alcohol. The catalyst is usually concentrated sulphuric acid. The alcohol's oxygen atom is protonated via an acid‐base reaction, leading to the formation of an oxonium ion. For example, when ethanol is treated with a limited amount of. Web learning objectives by the end of this section, you will be able.
Alcohols Can Act As Acids Or Bases (And Why It Matters)
Ethyl alcohol reacts with alumina at 260 0c and gives diethyl ether. Web it should say ethers. Web first, the strong acid protonates the ether oxygen. For example, when ethanol is treated with a limited amount of. The alcohol's oxygen atom is protonated via an acid‐base reaction, leading to the formation of an oxonium ion.
Web Identify The Reagents Needed To Prepare A Given Ether Through A Williamson Synthesis.
For example, when ethanol is treated with a limited amount of. Web ethers can be prepared from organic compounds by various methods. [noun] a compound that is both an ether and an alcohol. Web we will see that alcohols and ethers must be “activated” before they can undergo a substitution or elimination reaction.
Describe The Structure And Properties Of Alcohols Describe The Structure And Properties Of Ethers.
Okay, but it's going to form on lee symmetrical ethers, okay? Web the first name is the common name, in which you put the names of the alkyl groups before the word ether. Web esters are produced when carboxylic acids are heated with alcohols in the presence of an acid catalyst. Web learning objectives by the end of this section, you will be able to:
Web First, The Strong Acid Protonates The Ether Oxygen.
Identify the limitations of the williamson synthesis, and make the appropriate. Some of them are discussed below, preparation of ethers by alcohol dehydration in this method, in the. Web ethers can be obtained from alcohols by the elimination of a molecule of water from two molecules of the alcohol. And the reason is because we're always gonna be reacting acid in alcohol and you're gonna.
Sulfuric Acid Dissociates, Giving A Proton Plus The Bisulfate Ion.
Web it should say ethers. The alcohol's oxygen atom is protonated via an acid‐base reaction, leading to the formation of an oxonium ion. (organic compound, uncountable) diethyl ether (c 4 h 10 o), a. Ethyl alcohol reacts with alumina at 260 0c and gives diethyl ether.