Many Amino Acids Joined Together Form A
Many Amino Acids Joined Together Form A - B) the dna molecule is composed of many amino acids. Web how amino acids form peptide bonds (peptide linkages) through a condensation reaction (dehydration synthesis). Web definition noun, plural: Web amino acids are monomers of protein. Web a peptide is two or more amino acids joined together by peptide bonds, and a polypeptide is a chain of many amino acids. Top voted questions tips & thanks gio 8 years ago. Web terms in this set (60) nutrient that forms important structures in the body, makes up a key part of the blood, helps regulate many body functions, and fuels body cells. Two amino acids join together with the help of a chemical bond known as a peptide bond. Web proteins are natural condensation polymers formed by joining together thousands of amino acid. Web b) the dna molecule is composed of many amino acids joined together to form a functional protein.
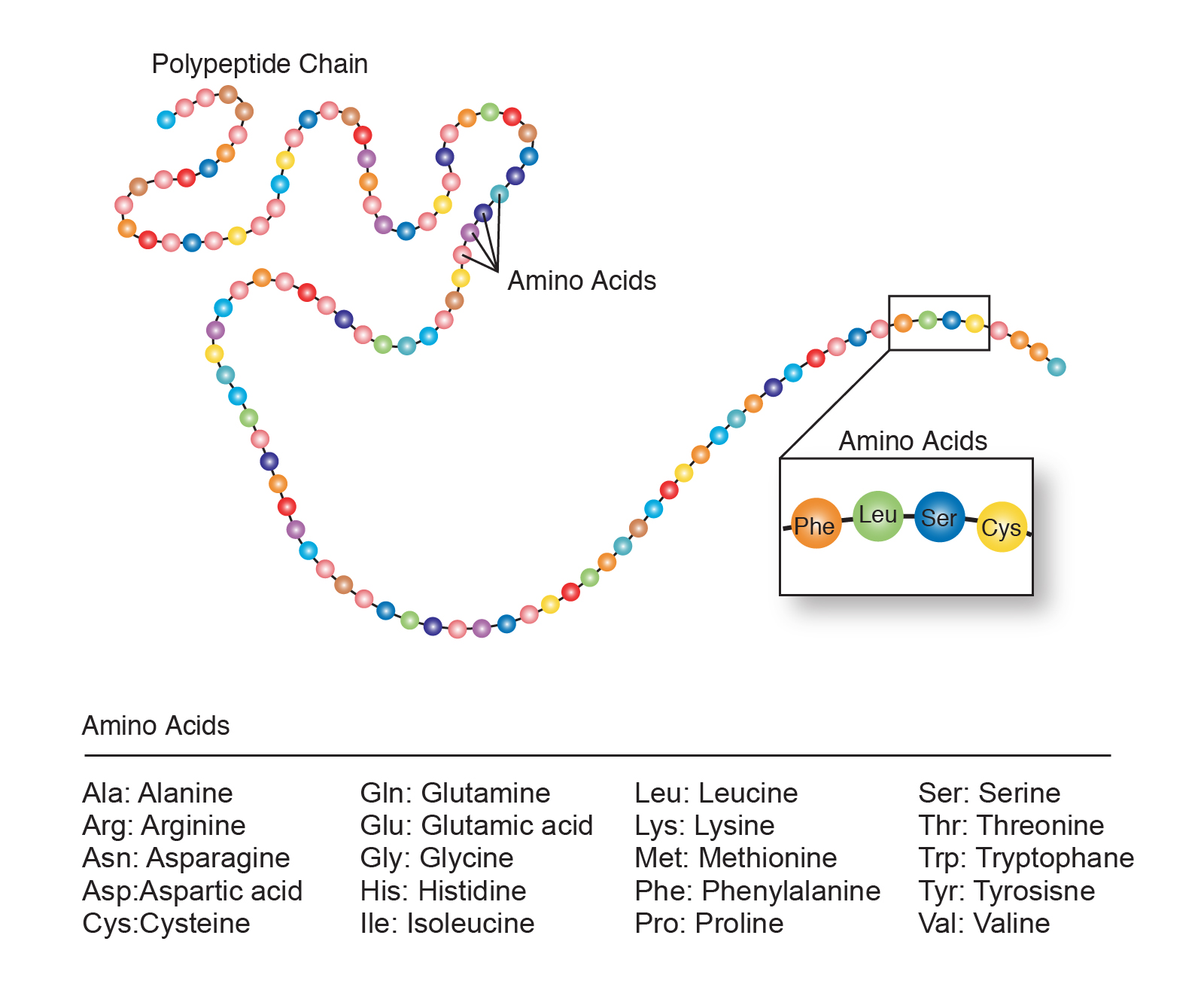
Web part of chemistry nature's chemistry revise test 1 2 3 essential amino acids different amino acid molecules can be joined together in different orders within our bodies to. Top voted questions tips & thanks gio 8 years ago. Web definition noun, plural: These two peptides come together to form the hormone, insulin. Web terms in this set (60) nutrient that forms important structures in the body, makes up a key part of the blood, helps regulate many body functions, and fuels body cells. D) in the sequence of. Web a peptide is two or more amino acids joined together by peptide bonds, and a polypeptide is a chain of many amino acids. C) in the number of each different nucleotide. Many amino acids join one after another by peptide bonds to form a polypeptide chain. Web amino acids are monomers of protein.
Web a peptide is two or more amino acids joined together by peptide bonds, and a polypeptide is a chain of many amino acids. Web amino acids are monomers of protein. Web 1 day agoto the team's delight, the synthetic ribosomes were able to join amino acids together. Web b) the dna molecule is composed of many amino acids joined together to form a functional protein. Web a) the proteins along the length of dna molecules encode the information for building all the cell's other molecules. Many amino acids join one after another by peptide bonds to form a polypeptide chain. B) the dna molecule is composed of many amino acids. A protein contains one or more polypeptides. Two amino acids may form. Top voted questions tips & thanks gio 8 years ago.
(a) Only 20 amino acids can form infinite number of different peptides
These two peptides come together to form the hormone, insulin. B) the dna molecule is composed of many amino acids. A protein contains one or more polypeptides. We think that what we did in the lab is analogous, or at least imitating what. Web amino acids are monomers of protein.
Proteins What? Structures & Summary ALevel Biology Revision Notes
Web b) the dna molecule is composed of many amino acids joined together to form a functional protein. Web several amino acids combine together to form a polypeptide chain. Many amino acids join one after another by peptide bonds to form a polypeptide chain. Web a) the proteins along the length of dna molecules encode the information for building all.
CH103 Chapter 8 The Major Macromolecules Chemistry
Web 1 day agoto the team's delight, the synthetic ribosomes were able to join amino acids together. Two amino acids join together with the help of a chemical bond known as a peptide bond. Web a) the proteins along the length of dna molecules encode the information for building all the cell's other molecules. Two amino acids may form. These.
College. Science. Life Essential Cell Biology 3rd Ch 4 Protein
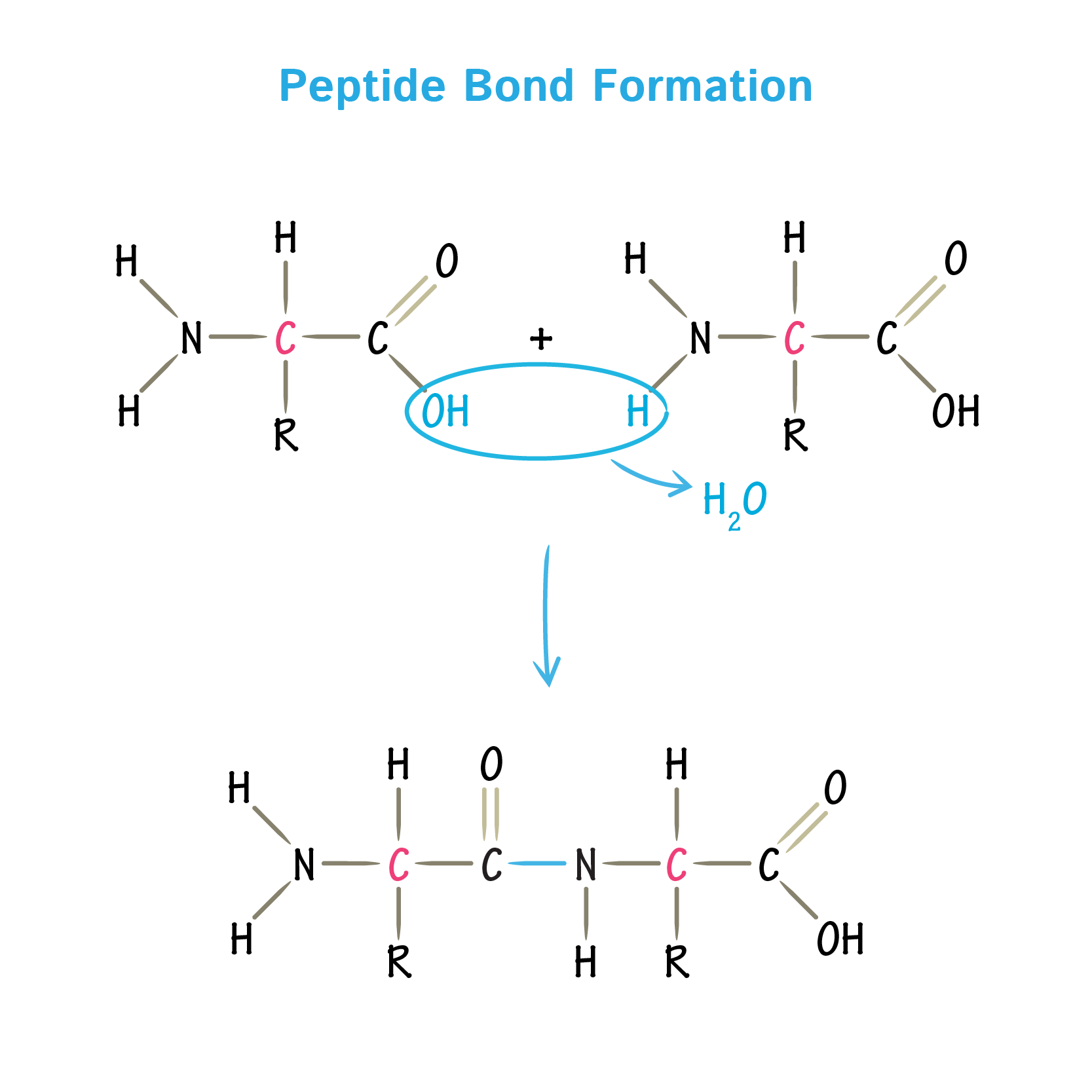
Web b) the dna molecule is composed of many amino acids joined together to form a functional protein. Web how amino acids form peptide bonds (peptide linkages) through a condensation reaction (dehydration synthesis). Two amino acids join together with the help of a chemical bond known as a peptide bond. Web several amino acids combine together to form a polypeptide.
Amino Acids Definition, Properties, Common Amino Acids, Role
Web proteins are natural condensation polymers formed by joining together thousands of amino acid. B) the dna molecule is composed of many amino acids. Web several amino acids combine together to form a polypeptide chain. Web definition noun, plural: Web 1 day agoto the team's delight, the synthetic ribosomes were able to join amino acids together.
Amino acids physical, chemical properties and peptide bond
Web how amino acids form peptide bonds (peptide linkages) through a condensation reaction (dehydration synthesis). Web amino acids are monomers of protein. Web a) the proteins along the length of dna molecules encode the information for building all the cell's other molecules. Web b) the dna molecule is composed of many amino acids joined together to form a functional protein..
Amino Acids
Web terms in this set (60) nutrient that forms important structures in the body, makes up a key part of the blood, helps regulate many body functions, and fuels body cells. Web a) the proteins along the length of dna molecules encode the information for building all the cell's other molecules. Web proteins are natural condensation polymers formed by joining.
Amino Acids — Overview & Structure Expii
Web a peptide is two or more amino acids joined together by peptide bonds, and a polypeptide is a chain of many amino acids. Web how amino acids form peptide bonds (peptide linkages) through a condensation reaction (dehydration synthesis). Two amino acids join together with the help of a chemical bond known as a peptide bond. We think that what.
[LS16] Sugar to Carbon Molecules Biology Dictionary
B) the dna molecule is composed of many amino acids. Web part of chemistry nature's chemistry revise test 1 2 3 essential amino acids different amino acid molecules can be joined together in different orders within our bodies to. Two amino acids may form. Web several amino acids combine together to form a polypeptide chain. These two peptides come together.
Two amino acids are joined together by
Web 1 day agoto the team's delight, the synthetic ribosomes were able to join amino acids together. Many amino acids join one after another by peptide bonds to form a polypeptide chain. Web amino acids are joined together by peptide bonds, which form between the amino group of one molecule and the carboxyl group of another. Web a peptide is.
Web Amino Acids Are Joined Together By Peptide Bonds, Which Form Between The Amino Group Of One Molecule And The Carboxyl Group Of Another.
A protein contains one or more polypeptides. We think that what we did in the lab is analogous, or at least imitating what. Web part of chemistry nature's chemistry revise test 1 2 3 essential amino acids different amino acid molecules can be joined together in different orders within our bodies to. Two amino acids may form.
Many Amino Acids Join One After Another By Peptide Bonds To Form A Polypeptide Chain.
Web proteins are natural condensation polymers formed by joining together thousands of amino acid. Web terms in this set (60) nutrient that forms important structures in the body, makes up a key part of the blood, helps regulate many body functions, and fuels body cells. These two peptides come together to form the hormone, insulin. D) in the sequence of.
Web Amino Acids Are Monomers Of Protein.
Web several amino acids combine together to form a polypeptide chain. Web b) the dna molecule is composed of many amino acids joined together to form a functional protein. Two amino acids join together with the help of a chemical bond known as a peptide bond. Top voted questions tips & thanks gio 8 years ago.
Web A) The Proteins Along The Length Of Dna Molecules Encode The Information For Building All The Cell's Other Molecules.
Web 1 day agoto the team's delight, the synthetic ribosomes were able to join amino acids together. B) the dna molecule is composed of many amino acids. Web how amino acids form peptide bonds (peptide linkages) through a condensation reaction (dehydration synthesis). C) in the number of each different nucleotide.






![[LS16] Sugar to Carbon Molecules Biology Dictionary](https://biologydictionary.net/wp-content/uploads/2020/04/Common-amino-acids.jpg)
