Nvme Form Factor
Nvme Form Factor - The most common form factors are: The latest type of ssd available is the m.2 nvme ssd. Web nvme supports up to 10 million iops, 16 gbps of throughput, less than 10 microseconds of latency, 65,535 queues and 65,536 commands per queue. Understanding the various form factors is important. Web no, m.2 and nvme aren't the same, but they work in conjunction with each other. Web nvme drives come in lots of different form factors, generally driven by their market segment. M.2 replaces the msata standard, which uses the pci express mini card physical card layout and connectors. Web m.2, pronounced m dot two and formerly known as the next generation form factor (ngff), is a specification for internally mounted computer expansion cards and associated connectors. Web m.2 nvme ssds. Combining the faster nvme interface with the compact m.2 form factor, it offers high levels of performance with up to 5,500 mb/s sequential read speeds.
Web m.2, pronounced m dot two and formerly known as the next generation form factor (ngff), is a specification for internally mounted computer expansion cards and associated connectors. The most common form factors are: M.2 replaces the msata standard, which uses the pci express mini card physical card layout and connectors. Web nvme supports up to 10 million iops, 16 gbps of throughput, less than 10 microseconds of latency, 65,535 queues and 65,536 commands per queue. Understanding the various form factors is important. The latest type of ssd available is the m.2 nvme ssd. Atp m.2 2280 nvme ssd specifications m.2 type 1620 hsbga. Web nvme ssd deployments are surging, fueling the need for new capacities, performance, power, connectivity and form factors. Designed for flash, nvme's speed and low latency leave sata in the dust and enable much higher storage capacities in smaller form factors such as m.2. Combining the faster nvme interface with the compact m.2 form factor, it offers high levels of performance with up to 5,500 mb/s sequential read speeds.
Combining the faster nvme interface with the compact m.2 form factor, it offers high levels of performance with up to 5,500 mb/s sequential read speeds. Web m.2 nvme ssds. The latest type of ssd available is the m.2 nvme ssd. Understanding the various form factors is important. Designed for flash, nvme's speed and low latency leave sata in the dust and enable much higher storage capacities in smaller form factors such as m.2. The most common form factors are: Heatsink ball grid array (hsbga) ssds are atp’s tiniest flash storage solutions supporting the nvme protocol. Nvme is much faster because it provides more bandwidth than sata models which improves performance in heavier productivity applications. Web nvme supports up to 10 million iops, 16 gbps of throughput, less than 10 microseconds of latency, 65,535 queues and 65,536 commands per queue. Web no, m.2 and nvme aren't the same, but they work in conjunction with each other.
NVMe SSDs Ready to Embrace EDSFF Form Factors EE Times Asia
Combining the faster nvme interface with the compact m.2 form factor, it offers high levels of performance with up to 5,500 mb/s sequential read speeds. Web nvme drives come in lots of different form factors, generally driven by their market segment. Heatsink ball grid array (hsbga) ssds are atp’s tiniest flash storage solutions supporting the nvme protocol. The most common.
SSD M.2 Nvme 512GB 2242 Double Cut (Form Factor 2242) OSCOO
Web no, m.2 and nvme aren't the same, but they work in conjunction with each other. M.2 is the ssd form factor, while nvme is the interface that connects it to the motherboard. Heatsink ball grid array (hsbga) ssds are atp’s tiniest flash storage solutions supporting the nvme protocol. Web nvme ssd deployments are surging, fueling the need for new.
(PR) Greenliant Releases EnduroSLC SSDs in U.2 NVMe Formfactor PotatoPC
Atp m.2 2280 nvme ssd specifications m.2 type 1620 hsbga. Web m.2 nvme ssds. Web no, m.2 and nvme aren't the same, but they work in conjunction with each other. Understanding the various form factors is important. Nvme is much faster because it provides more bandwidth than sata models which improves performance in heavier productivity applications.
Toshiba Introduces New Tiny NVMe SSD Form Factor
Combining the faster nvme interface with the compact m.2 form factor, it offers high levels of performance with up to 5,500 mb/s sequential read speeds. Nvme is much faster because it provides more bandwidth than sata models which improves performance in heavier productivity applications. Web nvme ssd deployments are surging, fueling the need for new capacities, performance, power, connectivity and.
Inspiron 7773 which m.2 ssd are compatible Dell Community
M.2 is the ssd form factor, while nvme is the interface that connects it to the motherboard. Combining the faster nvme interface with the compact m.2 form factor, it offers high levels of performance with up to 5,500 mb/s sequential read speeds. Web nvme supports up to 10 million iops, 16 gbps of throughput, less than 10 microseconds of latency,.
Meet EDSFF 1PB of flash storage in a single rack VentureBeat
Atp m.2 2280 nvme ssd specifications m.2 type 1620 hsbga. The most common form factors are: Understanding the various form factors is important. Heatsink ball grid array (hsbga) ssds are atp’s tiniest flash storage solutions supporting the nvme protocol. Web nvme supports up to 10 million iops, 16 gbps of throughput, less than 10 microseconds of latency, 65,535 queues and.
EDSFF Dynamic Family of Form Factors for Data Center SSDs YouTube
Web nvme ssd deployments are surging, fueling the need for new capacities, performance, power, connectivity and form factors. Web no, m.2 and nvme aren't the same, but they work in conjunction with each other. M.2 replaces the msata standard, which uses the pci express mini card physical card layout and connectors. Heatsink ball grid array (hsbga) ssds are atp’s tiniest.
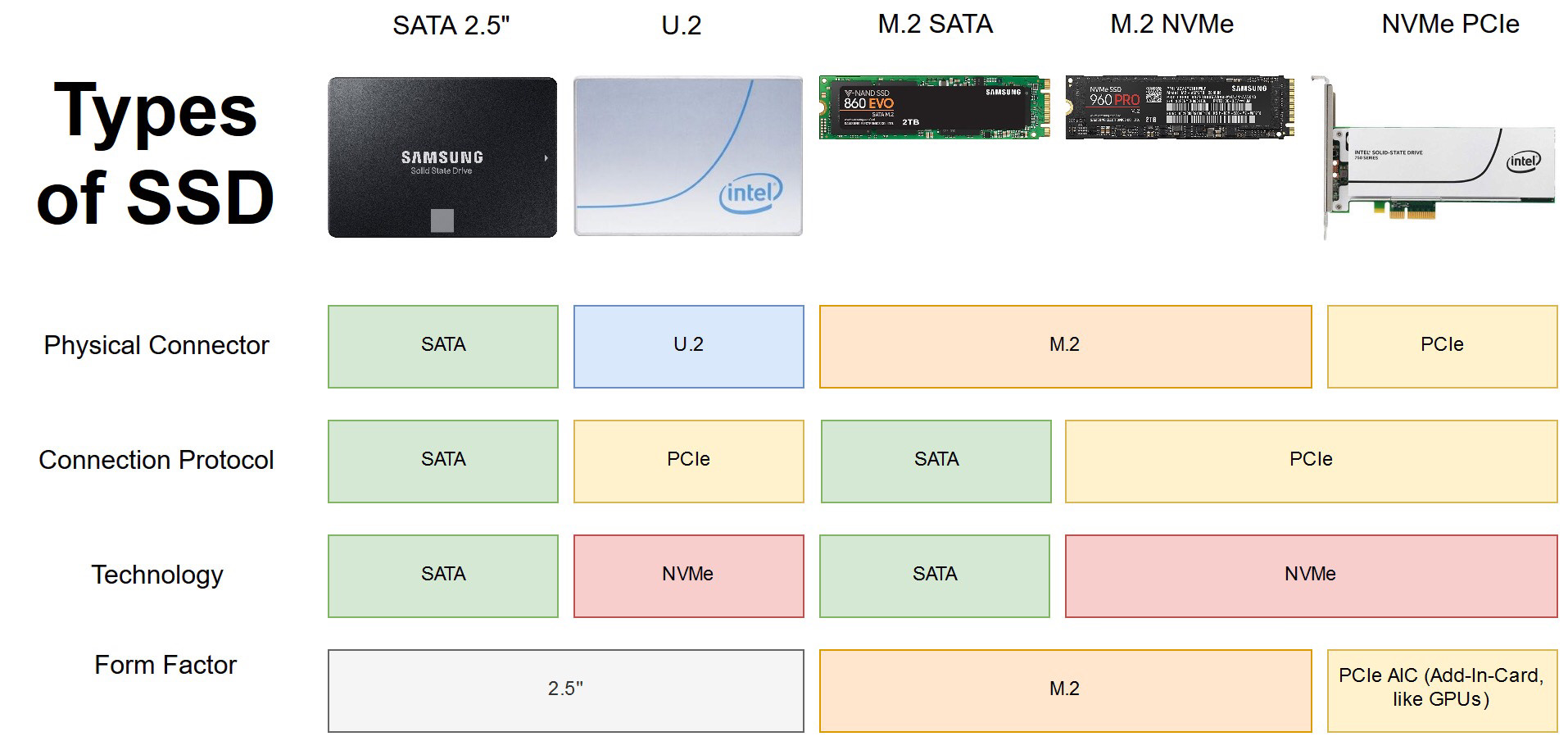
Different Types of SSDs Explained 2.5" / M.2, SATA / PCIe, NVMe
Heatsink ball grid array (hsbga) ssds are atp’s tiniest flash storage solutions supporting the nvme protocol. Web m.2, pronounced m dot two and formerly known as the next generation form factor (ngff), is a specification for internally mounted computer expansion cards and associated connectors. Understanding the various form factors is important. Atp m.2 2280 nvme ssd specifications m.2 type 1620.
NVMe SSDs New Features and Form Factors YouTube
Heatsink ball grid array (hsbga) ssds are atp’s tiniest flash storage solutions supporting the nvme protocol. Web no, m.2 and nvme aren't the same, but they work in conjunction with each other. Web nvme supports up to 10 million iops, 16 gbps of throughput, less than 10 microseconds of latency, 65,535 queues and 65,536 commands per queue. M.2 replaces the.
(PR) Kioxia Demonstrates Next Generation NVMe SSD Form Factor for Cloud
Designed for flash, nvme's speed and low latency leave sata in the dust and enable much higher storage capacities in smaller form factors such as m.2. Heatsink ball grid array (hsbga) ssds are atp’s tiniest flash storage solutions supporting the nvme protocol. Nvme is much faster because it provides more bandwidth than sata models which improves performance in heavier productivity.
Web M.2, Pronounced M Dot Two And Formerly Known As The Next Generation Form Factor (Ngff), Is A Specification For Internally Mounted Computer Expansion Cards And Associated Connectors.
Web no, m.2 and nvme aren't the same, but they work in conjunction with each other. Web m.2 nvme ssds. Designed for flash, nvme's speed and low latency leave sata in the dust and enable much higher storage capacities in smaller form factors such as m.2. Atp m.2 2280 nvme ssd specifications m.2 type 1620 hsbga.
Combining The Faster Nvme Interface With The Compact M.2 Form Factor, It Offers High Levels Of Performance With Up To 5,500 Mb/S Sequential Read Speeds.
Nvme is much faster because it provides more bandwidth than sata models which improves performance in heavier productivity applications. Web nvme supports up to 10 million iops, 16 gbps of throughput, less than 10 microseconds of latency, 65,535 queues and 65,536 commands per queue. The most common form factors are: The latest type of ssd available is the m.2 nvme ssd.
Heatsink Ball Grid Array (Hsbga) Ssds Are Atp’s Tiniest Flash Storage Solutions Supporting The Nvme Protocol.
Understanding the various form factors is important. Here’s what you need to know about emerging form factors available for your new design. Web nvme drives come in lots of different form factors, generally driven by their market segment. M.2 is the ssd form factor, while nvme is the interface that connects it to the motherboard.
M.2 Replaces The Msata Standard, Which Uses The Pci Express Mini Card Physical Card Layout And Connectors.
Web nvme ssd deployments are surging, fueling the need for new capacities, performance, power, connectivity and form factors.