Which Amino Acids Can Form Disulfide Bonds
Which Amino Acids Can Form Disulfide Bonds - Disulfide bonds can be formed between cysteine residues within the same protein (intramolecular) or between proteins (intermolecular). Web the amino acid cysteine (cys) has a sulfhydryl (sh) group as a side chain. The a chain also contains an internal disulfide bond. Web the cysteine amino acid group is the only amino acid capable of forming disulfide bonds, and thus can only do so with other cysteine groups. Web is cysteine the only amino acid that can form disulfide bonds? Their other properties varying for each particular amino acid. Two disulfide bonds connect the a and b chains together, and a. Web we found that weakly hydrophilic and aromatic amino acids are quite abundant in the regions around disulfide bonds, contrary to aliphatic and hydrophobic amino acids. They can also be formed between the cysteine residue of a protein and a thiol of a small molecular weight compound like glutathione. Their solubility depends on the size and nature of the side chain.
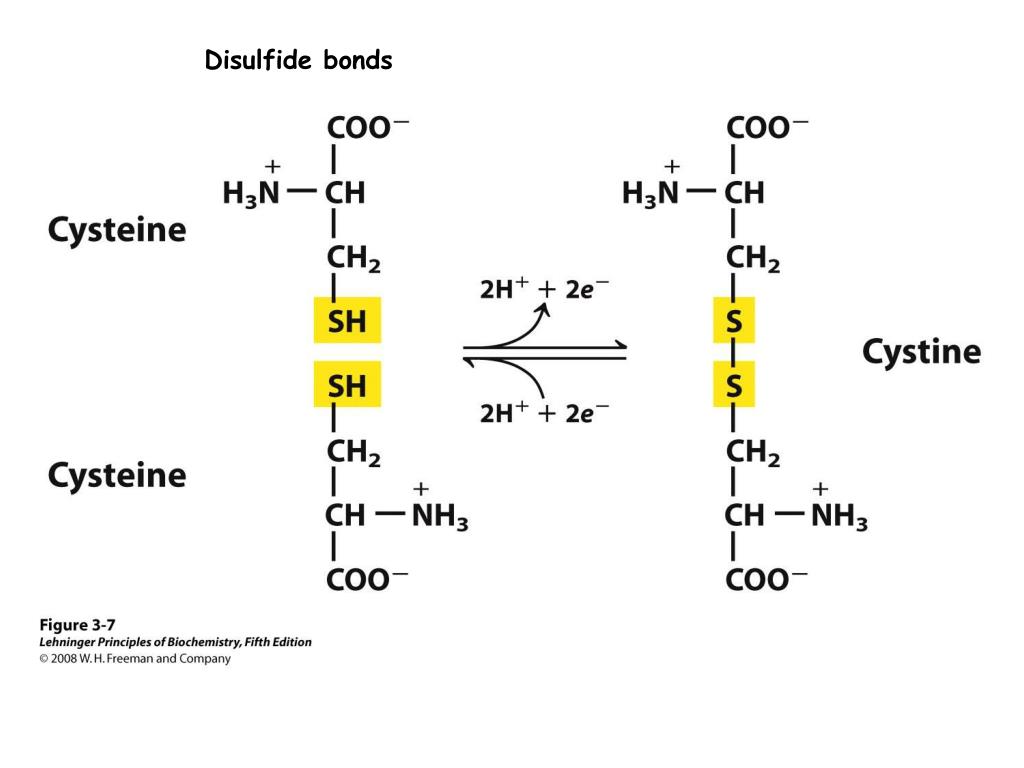
Disulfide bonds can be formed between cysteine residues within the same protein (intramolecular) or between proteins (intermolecular). Web is cysteine the only amino acid that can form disulfide bonds? Thus methionine is more hydrophobic, sterically. Most disulfide linkages are found in proteins destined for export or residence on the plasma membrane. The a chain also contains an internal disulfide bond. Web insulin consists of an a chain and a b chain. Web the cysteine amino acid group is the only amino acid capable of forming disulfide bonds, and thus can only do so with other cysteine groups. They can also be formed between the cysteine residue of a protein and a thiol of a small molecular weight compound like glutathione. Web we found that weakly hydrophilic and aromatic amino acids are quite abundant in the regions around disulfide bonds, contrary to aliphatic and hydrophobic amino acids. Web amino acids are crystalline solids which usually are water soluble and only sparingly dissoluble in organic solvents.
Web the amino acid cysteine (cys) has a sulfhydryl (sh) group as a side chain. Most disulfide linkages are found in proteins destined for export or residence on the plasma membrane. Two disulfide bonds connect the a and b chains together, and a. Their solubility depends on the size and nature of the side chain. Web amino acids are crystalline solids which usually are water soluble and only sparingly dissoluble in organic solvents. Disulfide bonds can be formed between cysteine residues within the same protein (intramolecular) or between proteins (intermolecular). Their other properties varying for each particular amino acid. The a chain also contains an internal disulfide bond. Disulfide bonds in proteins are formed between the thiol groups of cysteine residues by the process of oxidative folding. Web the cysteine amino acid group is the only amino acid capable of forming disulfide bonds, and thus can only do so with other cysteine groups.
PPT Disulfide Bonds PowerPoint Presentation ID165240
They can also be formed between the cysteine residue of a protein and a thiol of a small molecular weight compound like glutathione. Web insulin consists of an a chain and a b chain. Their other properties varying for each particular amino acid. Thus methionine is more hydrophobic, sterically. Web the cysteine amino acid group is the only amino acid.
Illustrated Glossary of Organic Chemistry Disulfide bridge
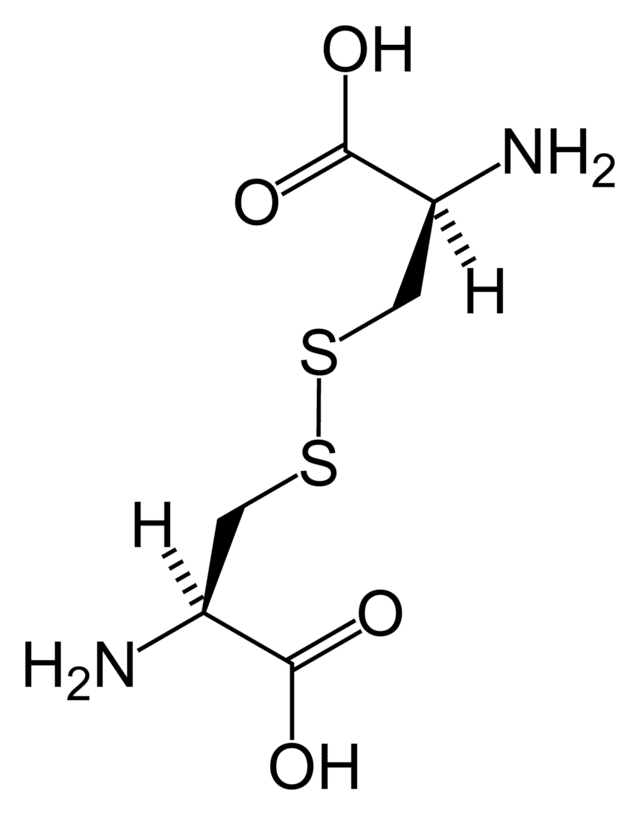
Web cystine is composed of two cysteines linked by a disulfide bond (shown here in its neutral form). Two disulfide bonds connect the a and b chains together, and a. The a chain also contains an internal disulfide bond. Thus methionine is more hydrophobic, sterically. Web amino acids are crystalline solids which usually are water soluble and only sparingly dissoluble.
Amino acid sequence of HsTX1[R14A] with four disulfide bonds indicated
Their solubility depends on the size and nature of the side chain. Two disulfide bonds connect the a and b chains together, and a. Their other properties varying for each particular amino acid. The a chain also contains an internal disulfide bond. Web amino acids are crystalline solids which usually are water soluble and only sparingly dissoluble in organic solvents.
Identify the true statements regarding disulfide bridges (disulfide
Web cystine is composed of two cysteines linked by a disulfide bond (shown here in its neutral form). Web is cysteine the only amino acid that can form disulfide bonds? Web amino acids are crystalline solids which usually are water soluble and only sparingly dissoluble in organic solvents. Disulfide bonds can be formed between cysteine residues within the same protein.
Disulfide bond wikidoc
Thus methionine is more hydrophobic, sterically. Web insulin consists of an a chain and a b chain. Their solubility depends on the size and nature of the side chain. They can also be formed between the cysteine residue of a protein and a thiol of a small molecular weight compound like glutathione. Disulfide bonds can be formed between cysteine residues.
A piece of a sequence of amino acids, with two disulfide bonds between
Web insulin consists of an a chain and a b chain. Web the amino acid cysteine (cys) has a sulfhydryl (sh) group as a side chain. Their other properties varying for each particular amino acid. Thus methionine is more hydrophobic, sterically. Their solubility depends on the size and nature of the side chain.
PPT Amino acids/Proteins PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID
Web is cysteine the only amino acid that can form disulfide bonds? Two disulfide bonds connect the a and b chains together, and a. The a chain also contains an internal disulfide bond. Web the cysteine amino acid group is the only amino acid capable of forming disulfide bonds, and thus can only do so with other cysteine groups. Thus.
Geometry of a disulfide bond. The covalent bond between the sulfur
Disulfide bonds can be formed between cysteine residues within the same protein (intramolecular) or between proteins (intermolecular). Their other properties varying for each particular amino acid. Web the cysteine amino acid group is the only amino acid capable of forming disulfide bonds, and thus can only do so with other cysteine groups. They can also be formed between the cysteine.
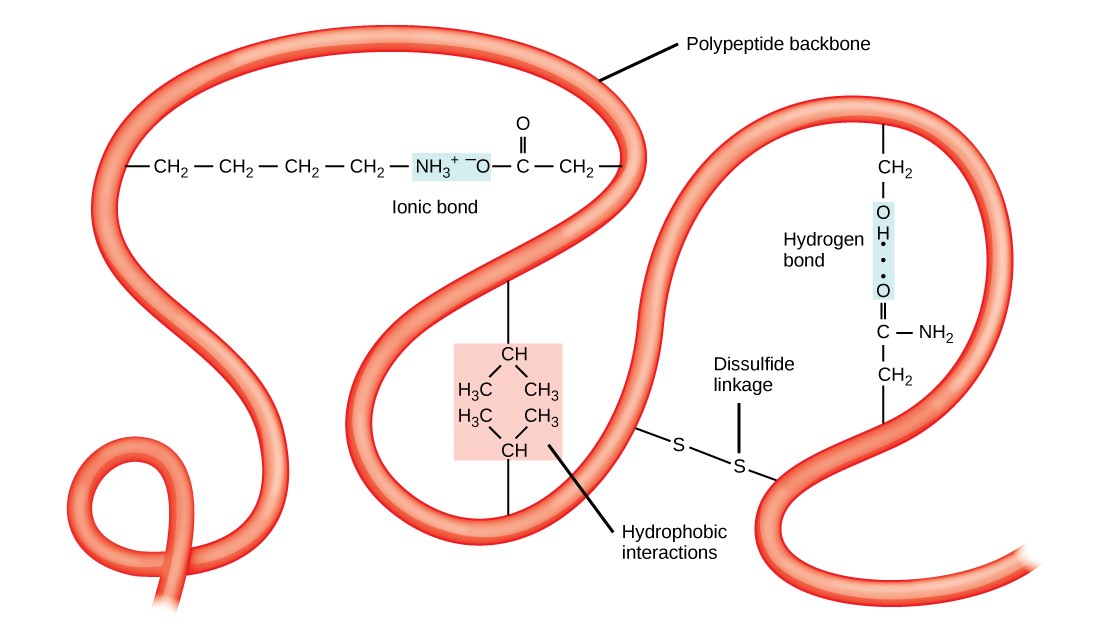
Chapter 3. Amino Acids & Proteins Introduction to Molecular and Cell
Web we found that weakly hydrophilic and aromatic amino acids are quite abundant in the regions around disulfide bonds, contrary to aliphatic and hydrophobic amino acids. Web cystine is composed of two cysteines linked by a disulfide bond (shown here in its neutral form). Disulfide bonds in proteins are formed between the thiol groups of cysteine residues by the process.
Chapter 2 Protein Structure Chemistry
Web insulin consists of an a chain and a b chain. Disulfide bonds can be formed between cysteine residues within the same protein (intramolecular) or between proteins (intermolecular). Their solubility depends on the size and nature of the side chain. Web we found that weakly hydrophilic and aromatic amino acids are quite abundant in the regions around disulfide bonds, contrary.
Thus Methionine Is More Hydrophobic, Sterically.
The a chain also contains an internal disulfide bond. Web is cysteine the only amino acid that can form disulfide bonds? Disulfide bonds can be formed between cysteine residues within the same protein (intramolecular) or between proteins (intermolecular). Web insulin consists of an a chain and a b chain.
Web The Amino Acid Cysteine (Cys) Has A Sulfhydryl (Sh) Group As A Side Chain.
Most disulfide linkages are found in proteins destined for export or residence on the plasma membrane. Two disulfide bonds connect the a and b chains together, and a. Disulfide bonds in proteins are formed between the thiol groups of cysteine residues by the process of oxidative folding. They can also be formed between the cysteine residue of a protein and a thiol of a small molecular weight compound like glutathione.
Web Cystine Is Composed Of Two Cysteines Linked By A Disulfide Bond (Shown Here In Its Neutral Form).
Web the cysteine amino acid group is the only amino acid capable of forming disulfide bonds, and thus can only do so with other cysteine groups. Their solubility depends on the size and nature of the side chain. Their other properties varying for each particular amino acid. Web amino acids are crystalline solids which usually are water soluble and only sparingly dissoluble in organic solvents.
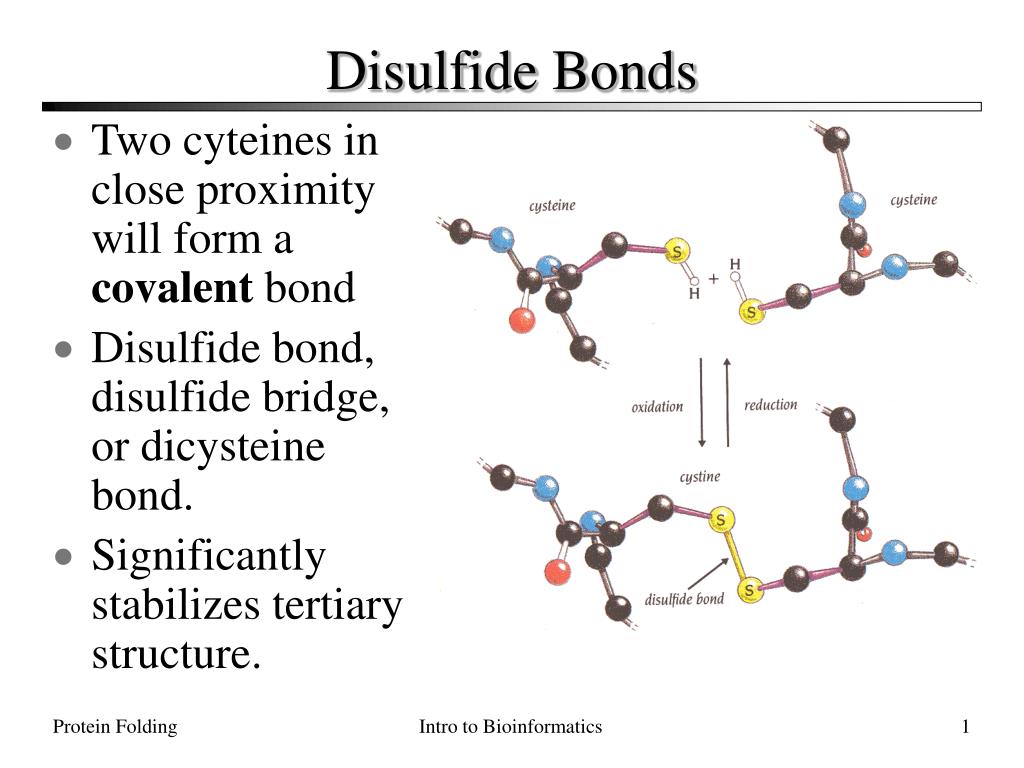
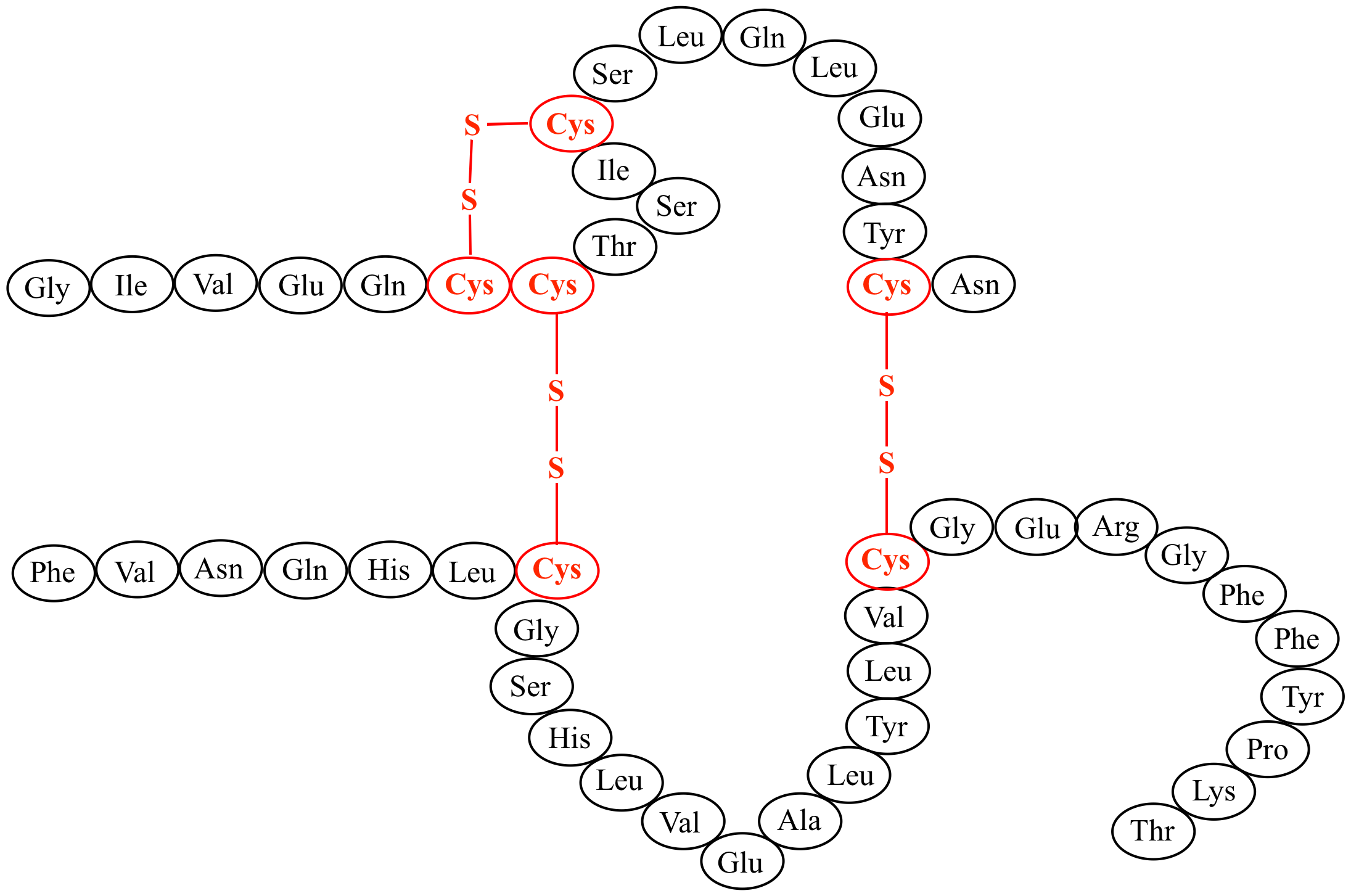
![Amino acid sequence of HsTX1[R14A] with four disulfide bonds indicated](https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Michael_Pennington/publication/320006041/figure/download/fig4/AS:542598037491712@1506376861314/Amino-acid-sequence-of-HsTX1R14A-with-four-disulfide-bonds-indicated-The-structure-of.png)