The Reduced Form Of The Electron Acceptor In Glycolysis Is
The Reduced Form Of The Electron Acceptor In Glycolysis Is - Fewer protons are pumped across the inner mitochondrial membrane when fadh2 is the. Such a compound is often referred to as an electron acceptor. Web the reduced form of the electron acceptor in glycolysis is | 1. Web when a compound accepts (gains) electrons, that compound becomes blank. Glycolysis produces 2 atp per glucose molecule, and hence. To form additional nadh b. 1 when a compound donates electrons the compound becomes oxidized.such a. Post any question and get expert. Oxygen is consumed as a reactant along with the organic fuel. Depending on the microcellular environment.
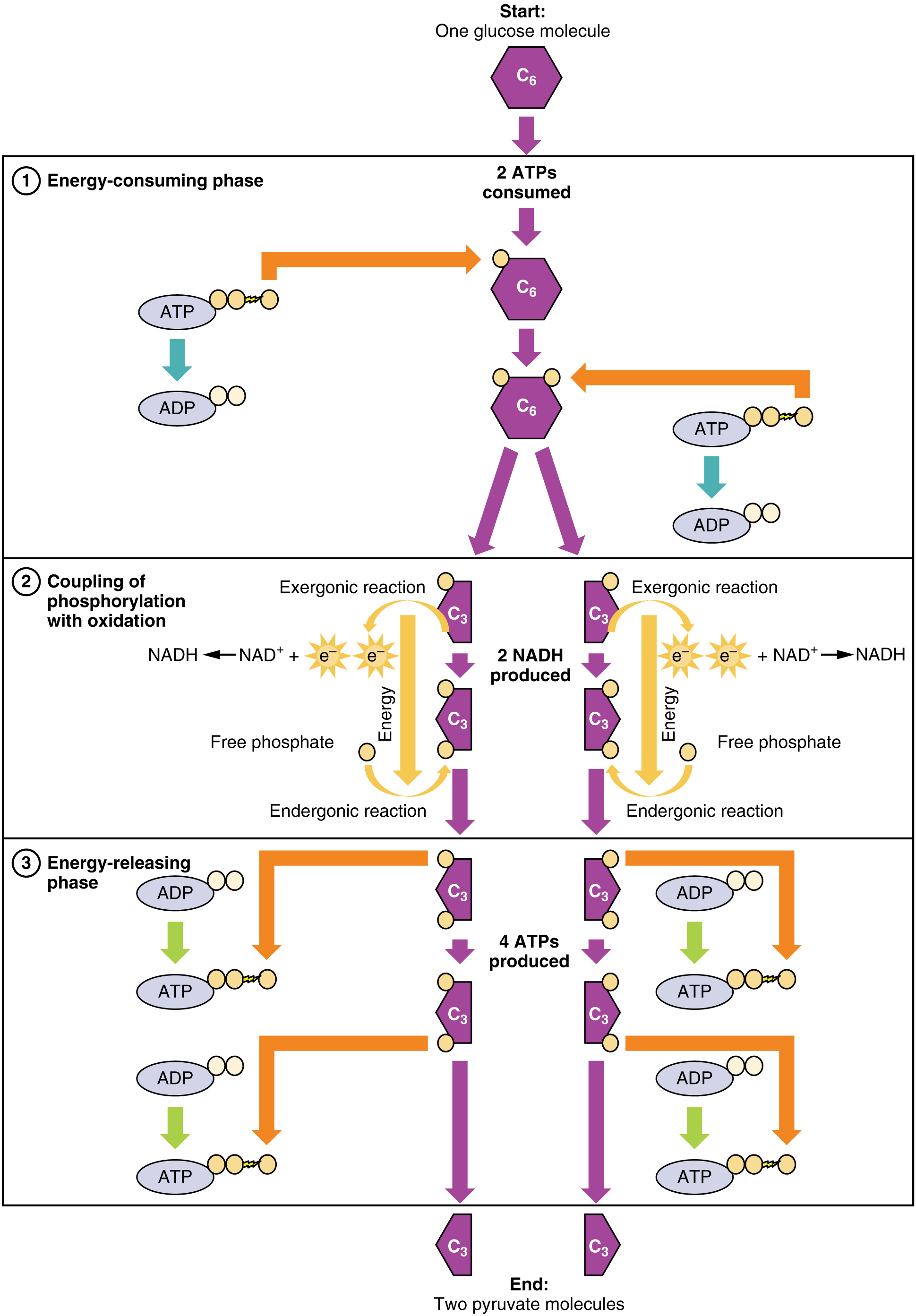
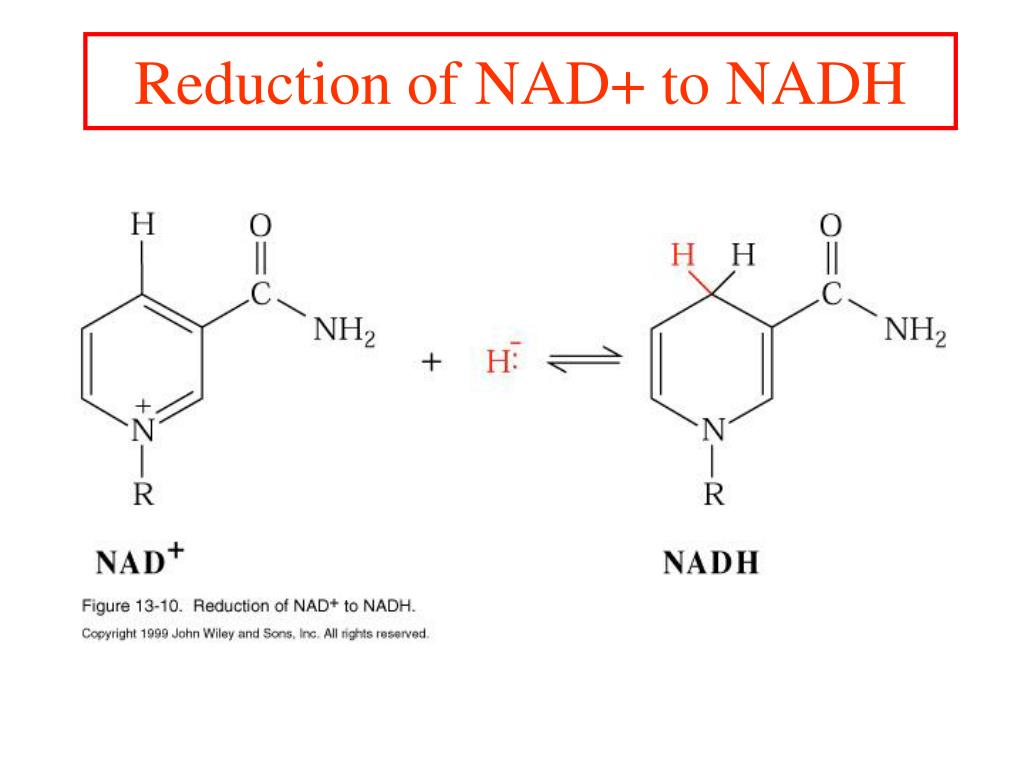
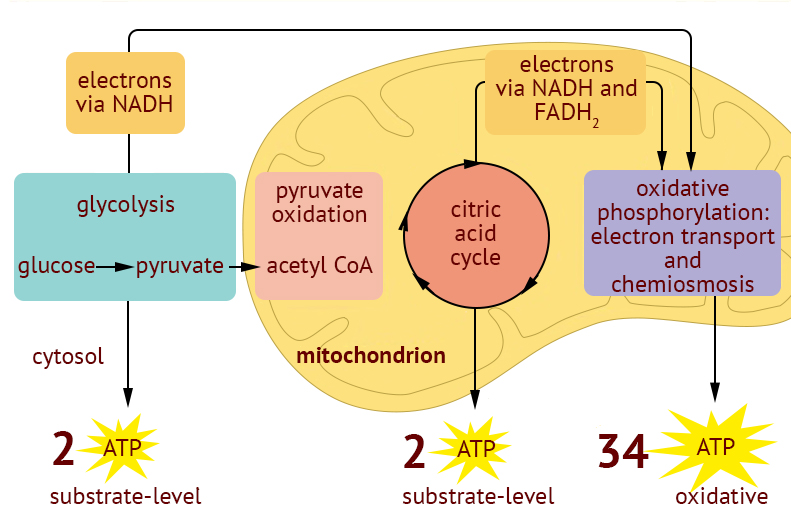
Web through the process of glycolysis, one molecule of glucose breaks down to form two molecules of pyruvate. Fewer protons are pumped across the inner mitochondrial membrane when fadh2 is the. Web nad+ is an oxidizing cofactor necessary to maintain the flow of glucose through glycolysis. Web when a compound accepts (gains) electrons, that compound becomes blank. 1 when a compound donates electrons the compound becomes oxidized.such a compound is referred to as. To form additional nadh b. Web nadh (electron carrier) is the reduced form of nad+ (which is an electron acceptor) and can be generated from glycolysis and other metabolic pathways. Web the reduced form of the electron acceptor in glycolysis is previous question next question not the exact question you're looking for? Glycolysis produces 2 atp per glucose molecule, and hence. Web once the electron donor in glycolysis gives up its electrons, it is oxidized to a compound called _______.
Both electron transport and atp synthesis would stop. Web a partial degradation of sugars or other organic fule that occurs without the use of oxygen. Such a compound is often referred to as an electron acceptor. Web the reduced form of the electron acceptor in glycolysis is | 1. Post any question and get expert. Fewer protons are pumped across the inner mitochondrial membrane when fadh2 is the. Web when a compound accepts (gains) electrons, that compound becomes blank. _________ is the compound that functions as the. Nadh (electron carrier) is the reduced form of nad+ (which is an electron acceptor) and can be generated from glycolysis and other metabolic pathways. Oxygen is consumed as a reactant along with the organic fuel.
The electron transport chain. Biochemistry, Electron transport chain
Web once the electron donor in glycolysis gives up its electrons, it is oxidized to a compound called _______. To form additional nadh b. Nadh (electron carrier) is the reduced form of nad+ (which is an electron acceptor) and can be generated from glycolysis and other metabolic pathways. To regenerate glucose if the appropriate final. Web nadh (electron carrier) is.
Solved e 1. An intermediate electron acceptor for oxidations
Web nadh (electron carrier) is the reduced form of nad+ (which is an electron acceptor) and can be generated from glycolysis and other metabolic pathways. Web the reduced form of the electron acceptor in glycolysis is | 1. To regenerate glucose if the appropriate final. Web once the electron donor in glycolysis gives up its electrons, it is oxidized to.
Making energy available — cellular respiration It's a natural universe
Web nad+ is an oxidizing cofactor necessary to maintain the flow of glucose through glycolysis. Such a compound is often referred to as an electron acceptor. Web the reduced form of the electron acceptor in glycolysis is | 1. Web when a compound accepts (gains) electrons, that compound becomes blank. To regenerate glucose if the appropriate final.
PPT Metabolism II and Glycolysis 5/7/03 PowerPoint Presentation, free
Web a partial degradation of sugars or other organic fule that occurs without the use of oxygen. Web nad+ is an oxidizing cofactor necessary to maintain the flow of glucose through glycolysis. Fewer protons are pumped across the inner mitochondrial membrane when fadh2 is the. Such a compound is often referred to as an electron acceptor. Glycolysis produces 2 atp.
Solved As A Result Of Glycolysis, There Is A Net Gain Of
Web when a compound accepts (gains) electrons, that compound becomes blank. Web glycolysis is the first step in the breakdown of glucose to extract energy for cellular metabolism. Both electron transport and atp synthesis would stop. Fewer protons are pumped across the inner mitochondrial membrane when fadh2 is the. 1 when a compound donates electrons the compound becomes oxidized.such a.
Electron Transport Chain and Oxidative Phosphorylation Biology Dictionary
Both electron transport and atp synthesis would stop. Web when a compound accepts (gains) electrons, that compound becomes blank. Nadh (electron carrier) is the reduced form of nad+ (which is an electron acceptor) and can be generated from glycolysis and other metabolic pathways. Web once the electron donor in glycolysis gives up its electrons, it is oxidized to a compound.
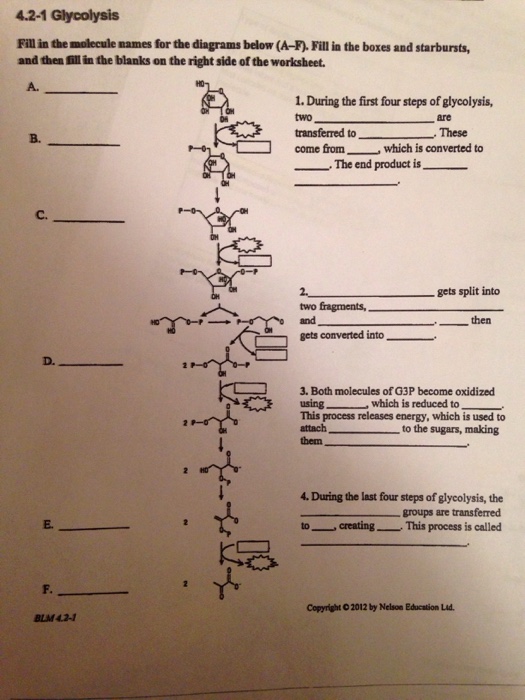
Solved 4.21 Glycolysis Fill In The Molecule Names For Th...
1 when a compound donates electrons the compound becomes oxidized.such a. Fewer protons are pumped across the inner mitochondrial membrane when fadh2 is the. Oxygen is consumed as a reactant along with the organic fuel. Depending on the microcellular environment. Web glycolysis is the first step in the breakdown of glucose to extract energy for cellular metabolism.
Electron Transport Chain — Summary & Diagrams Expii
Web nad+ is an oxidizing cofactor necessary to maintain the flow of glucose through glycolysis. 1 when a compound donates electrons the compound becomes oxidized.such a. Oxygen is consumed as a reactant along with the organic fuel. Web the reduced form of the electron acceptor in glycolysis is | 1. Glycolysis produces 2 atp per glucose molecule, and hence.
09. What goes into the Krebs cycle a. Acetyl c. Pyruvate Q9. What is
1 when a compound donates electrons the compound becomes oxidized.such a. Such a compound is often referred to as an electron acceptor. Web nadh (electron carrier) is the reduced form of nad+ (which is an electron acceptor) and can be generated from glycolysis and other metabolic pathways. _________ is the compound that functions as the. Web once the electron donor.
Solved We Used The Figure Below To Diagram The Inputs And...
Web a partial degradation of sugars or other organic fule that occurs without the use of oxygen. Post any question and get expert. Glycolysis produces 2 atp per glucose molecule, and hence. Web through the process of glycolysis, one molecule of glucose breaks down to form two molecules of pyruvate. Web the reduced form of the electron acceptor in glycolysis.
Glycolysis Produces 2 Atp Per Glucose Molecule, And Hence.
Fewer protons are pumped across the inner mitochondrial membrane when fadh2 is the. 1 when a compound donates electrons the compound becomes oxidized.such a compound is referred to as. Web when a compound accepts (gains) electrons, that compound becomes blank. 1 when a compound donates electrons the compound becomes oxidized.such a.
Web The Reduced Form Of The Electron Acceptor In Glycolysis Is Previous Question Next Question Not The Exact Question You're Looking For?
Both electron transport and atp synthesis would stop. Web a partial degradation of sugars or other organic fule that occurs without the use of oxygen. To regenerate glucose if the appropriate final. Web nad+ is an oxidizing cofactor necessary to maintain the flow of glucose through glycolysis.
Post Any Question And Get Expert.
Web through the process of glycolysis, one molecule of glucose breaks down to form two molecules of pyruvate. Such a compound is often referred to as an electron acceptor. Depending on the microcellular environment. Web nadh (electron carrier) is the reduced form of nad+ (which is an electron acceptor) and can be generated from glycolysis and other metabolic pathways.
Web Once The Electron Donor In Glycolysis Gives Up Its Electrons, It Is Oxidized To A Compound Called _______.
Oxygen is consumed as a reactant along with the organic fuel. Web the reduced form of the electron acceptor in glycolysis is | 1. Nadh (electron carrier) is the reduced form of nad+ (which is an electron acceptor) and can be generated from glycolysis and other metabolic pathways. To form additional nadh b.